110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

已发表论文
中国非输血依赖性地中海贫血患者中异常葡萄糖稳态的患病率
Authors Luo Y, Bajoria R, Lai Y, Pan H, Li Q, Zhang Z, Yang P, Chatterjee R, Liang Y
Received 3 December 2018
Accepted for publication 13 February 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 457—468
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S194591
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Juei-Tang Cheng
Purpose: To determine the prevalence and underlying
pathology of abnormal glucose homeostasis in Chinese patients with
non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia (NTDT).
Patients and methods: In this study, we enrolled 211 patients aged 4–63 years with NTDT, including 79 β thalassemia intermedia patients, 114 Hb H disease patients and 18 Hb E/β thalassemia patients. All had oral glucose tolerance test, serum ferritin (SF), homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) and liver iron concentration (LIC) measurement. One hundred and twenty healthy age-matched controls were also used for the comparative purpose. Iron load was assessed by using SF and hepatic load by LIC using validated MRI techniques.
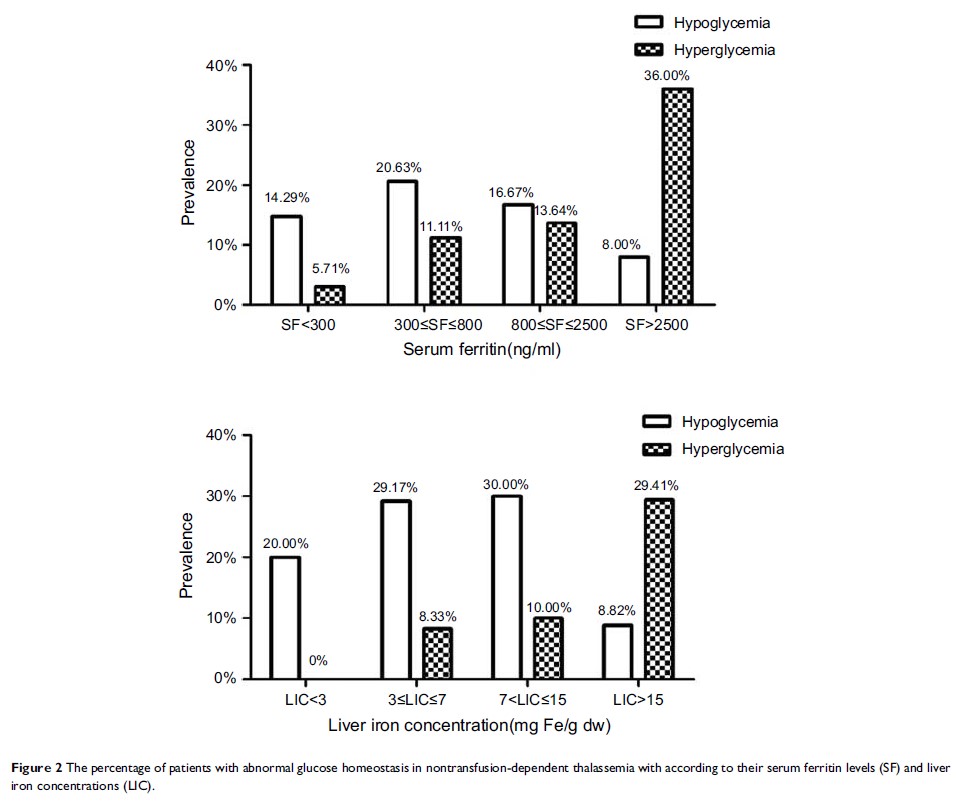
Results: The 211 patients were divided into three groups according to their fasting and 2 hrs postprandial blood glucose levels: hypoglycemic, normal glucose tolerance (NGT) and hyperglycemic groups. In this study, 149 patients had NGT, 33 had hypoglycemia, 4 had diabetes and 25 had impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). None had impaired fasting glucose. There was a significant correlation between 2 hrs postprandial blood glucose levels and age, PINS120, HOMA-IR, alanine aminotransferase and LIC (P <0.05). Risk factors for IGT in NTDT patients were older age (≥24 years) and SF concentration of ≥2,500 ng/mL.
Conclusion: Age ≥24 years and SF ≥2,500 ng/mL of NTDT patients were at a greater risk for impaired glucose tolerance.
Keywords: glucose homeostasis, non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia, liver iron overload, post prandial hyperglycaemia
Patients and methods: In this study, we enrolled 211 patients aged 4–63 years with NTDT, including 79 β thalassemia intermedia patients, 114 Hb H disease patients and 18 Hb E/β thalassemia patients. All had oral glucose tolerance test, serum ferritin (SF), homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) and liver iron concentration (LIC) measurement. One hundred and twenty healthy age-matched controls were also used for the comparative purpose. Iron load was assessed by using SF and hepatic load by LIC using validated MRI techniques.
Results: The 211 patients were divided into three groups according to their fasting and 2 hrs postprandial blood glucose levels: hypoglycemic, normal glucose tolerance (NGT) and hyperglycemic groups. In this study, 149 patients had NGT, 33 had hypoglycemia, 4 had diabetes and 25 had impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). None had impaired fasting glucose. There was a significant correlation between 2 hrs postprandial blood glucose levels and age, PINS120, HOMA-IR, alanine aminotransferase and LIC (P <0.05). Risk factors for IGT in NTDT patients were older age (≥24 years) and SF concentration of ≥2,500 ng/mL.
Conclusion: Age ≥24 years and SF ≥2,500 ng/mL of NTDT patients were at a greater risk for impaired glucose tolerance.
Keywords: glucose homeostasis, non-transfusion-dependent thalassemia, liver iron overload, post prandial hyperglycaemia