110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对氨基水杨酸增加了结核分枝杆菌临床分离株中异烟肼的易感性
Authors Zhang T, Jiang G, Wen S, Huo F, Wang F, Huang H, Pang Y
Received 7 January 2019
Accepted for publication 1 March 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 825—829
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S200697
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sahil Khanna
Background: The purpose of
this work was to assess the activity of para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS) in
combination with isoniazid (INH) against clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB).
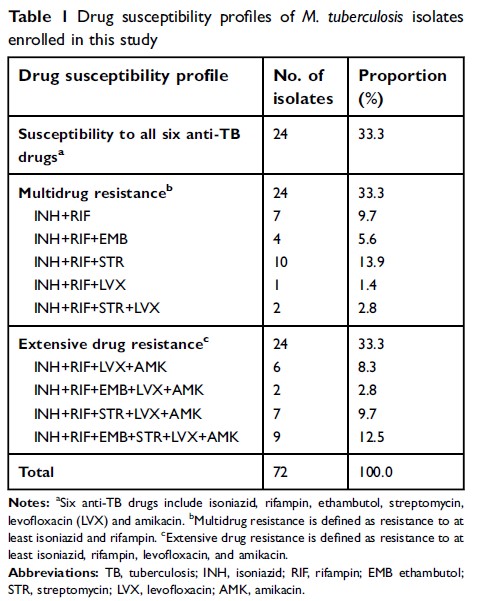
Materials and methods: A total of 72
MTB isolates with differential in vitro drug susceptibilities were included in
this study, comprising 24 pan-susceptible, 24 MDR-TB, and 24 extensively
drug-resistant (XDR) isolates. A microplate alamarBlue assay was performed to
identify the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of MTB isolates.
Results: The MIC50 of INH
was 4 mg/L, and that of PAS was 0.063 mg/L against MTB isolates when single
drug used. The combined use of INH and PAS resulted in 16-fold and 8-fold
decrease in MIC50 for INH and PAS, respectively. The
INH-PAS revealed synergistic activity in 94.4% of the isolates. In addition,
there was no significant difference in the FIC index of the INH-PAS combination
among individual isolates harboring different susceptibility pattern (P >0.05).
Conclusion: The
synergy between INH and PAS is demonstrated using non-multidrug-resistant
(non-MDR) and MDR-TB strains, which will provide clinicians with useful hints
to reuse this combination for treatment of TB patients in clinical practice.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis ,
isoniazid, para-aminosalicylic acid, synergy