110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

伞形酮经由 MAPK/NF-κB 通路对佐剂性关节炎大鼠的影响
Authors Ouyang L, Dan Y, Shao Z, Yang S, Yang C, Liu G, Zhou W, Duan D
Received 8 October 2018
Accepted for publication 5 February 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1163—1170
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S190155
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sukesh Voruganti
Purpose: Umbelliferone
(Umb), a member of coumarin family, is found in many plants and is a promising
molecule with potential anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative, and anti-tumor
activities. However, the effect of Umb on arthritis remains unclear.
Methods: A rat
model with Freund’s complete adjuvant (FCA)-induced arthritis was developed and
used to test the efficacy of Umb on arthritis rats. Rats were given an
intragastric injection of Umb (20 and 40 mg/kg) once daily from days 21 to
28 after the administration of FCA. Hind paw volume was assessed using a volume
meter. The pro-inflammatory cytokine levels and prostaglandin E2 (PEG2) level
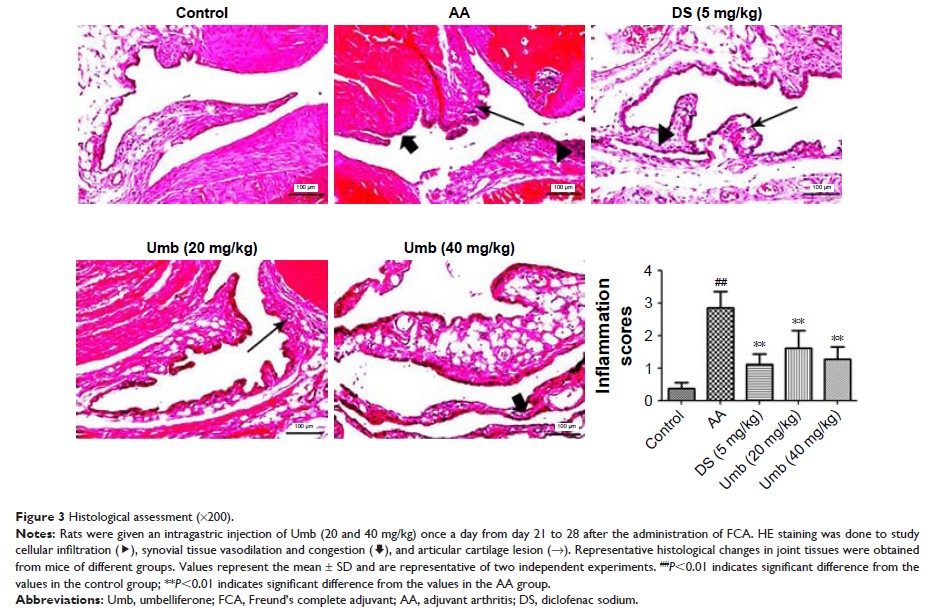
in serum and synovial fluid were detected by ELISA. HE staining was used to
determine representative histological changes in joint tissues, and Western
blot analysis was employed to study the effects of Umb on MAPK/NF-κB signaling
pathway.
Results: Our
results showed that Umb suppressed the release of IL-6, IL-1β, tumor necrosis
factor-alpha, and PEG2. In addition, Umb could also dramatically ameliorate the
pathological changes observed in rat joints. Based on the results of Western
blot, we also observed that Umb could strikingly suppress the expression of
MAPK/NF-κB pathway molecules.
Conclusion: These
results proved that treatment with Umb is very effective for arthritis and
inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathway may be a potential therapeutic
target for treatment of arthritis.
Keywords: umbelliferone,
arthritis, inflammation, MAPK/NF-κB pathway