110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PAFAH1B3 的异常表达与预后不良有关并会影响下咽鳞状细胞癌的增殖和侵袭性
Authors Xu J, Zang Y, Cao S, Lei D, Pan X
Received 28 November 2018
Accepted for publication 21 February 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2799—2808
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196324
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Background: Hypopharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma (HSCC) is among the most lethal tumors encountered in
the head and neck, and currently lacks satisfactory therapeutic targets.
Platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase 1B3 (PAFAH1B3), a cancer-relevant
metabolic driver, is reported to play a critical role in controlling
tumorigenesis and aggressiveness in several types of cancers. However, the role
of PAFAH1B3 in HSCC progression has not yet been identified.
Methods: The
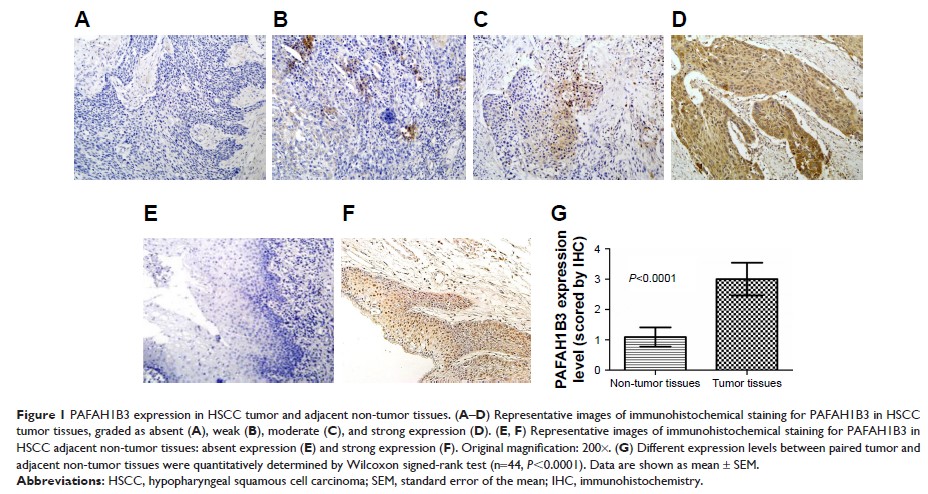
expression pattern of PAFAH1B3 was examined using immunohistochemistry in 83
HSCC tumor tissues and 44 paired adjacent non-tumor samples. Univariate and
multivariate analyses were conducted to explore its association with prognosis
of HSCC. In vitro loss-of-function assays were performed to explore the impact
of PAFAH1B3 knockdown on the biological phenotype of the human HSCC cell line,
ie, FaDu cells.
Results: PAFAH1B3
was overly expressed in the HSCC tumor tissues compared with the adjacent
non-tumor samples. Moreover, high expression of PAFAH1B3 was positively
correlated with cervical lymph node metastasis. PAFAH1B3 overexpression was
associated with poor outcome in HSCC, but it was not an independent prognostic
indicator. Furthermore, in vitro loss-of function experiments demonstrated that
PAFAH1B3 knockdown suppressed cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and
disrupting cell cycle process, and the migratory and invasive capacities were
also attenuated in the absence of PAFAH1B3.
Conclusion: This
study for the first time demonstrated the clinical value and the role of
PAFAH1B3 in the biological function of HSCC. This work suggested that PAFAH1B3
might serve as a potential therapeutic target for HSCC patients.
Keywords: hypopharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma, platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase 1B3,
prognosis, cell proliferation, migration, invasion