110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

高天冬氨酸转氨酶/丙氨酸转氨酶的比率可预测局部上尿路尿路上皮癌患者预后不良:在一个大型中国中心进行的倾向评分匹配研究
Authors Li Y, Fang D, Bao Z, He A, Guan B, He S, Zhan Y, Gong Y, Li X, Zhou L
Received 7 November 2018
Accepted for publication 17 February 2019
Published 11 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2635—2648
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193771
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Purpose: The aim
of this study was to evaluate the prognostic value of the aspartate
transaminase/alanine transaminase (AST/ALT) ratio in a large Chinese cohort
surgically treated for localized upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) using
propensity score matching (PSM) analysis.
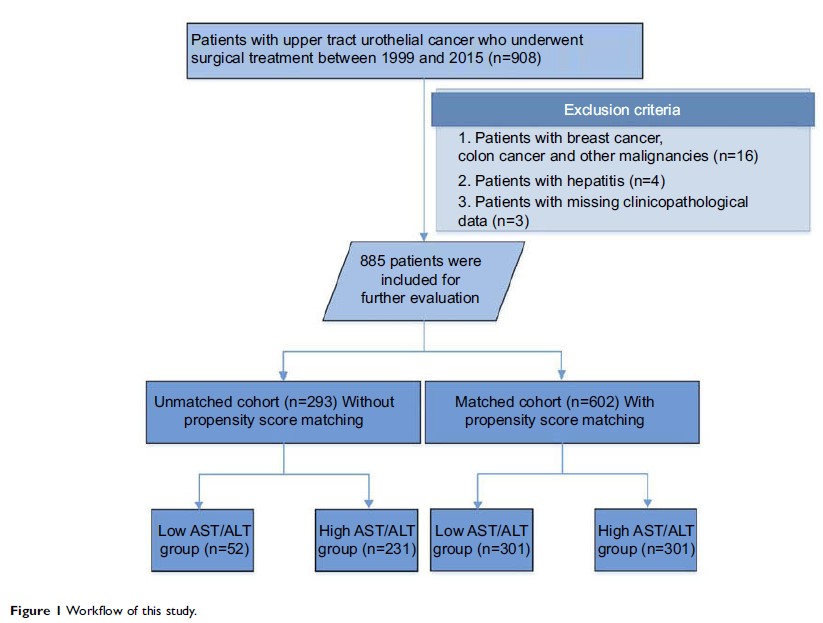
Methods: Data of
908 consecutive patients with localized UTUC who underwent radical
nephroureterectomy (RNU) were retrospectively evaluated. The endpoints of
prognosis were progression-free survival (PFS), cancer-specific survival (CSS)
and overall survival (OS) after RNU. We compared these endpoints according to
the AST/ALT ratio before and after 1:1 PSM. The independent predictors for PFS,
CSS and OS were also analyzed.
Results: A high
AST/ALT ratio was correlated with unfavorable factors, including elderly age,
female gender, history of coronary disease, alcohol and tobacco consumption,
lower body mass index, and larger tumor volume. Before PSM, the Kaplan–Meier
curves showed significantly poorer survival outcomes in PFS, CSS, and OS
(all P <0.001)
for patients with high AST/ALT ratios. After PSM, the high AST/ALT ratio group
also had significantly inferior survival outcomes in terms of PFS, OS and CSS
(all P <0.001).
Furthermore, multivariate analyses revealed that the AST/ALT ratio was an
independent predictor for PFS, CSS and OS before PSM (PFS hazard ratio [HR]
1.454, P =0.001;
CSS HR 2.577, P <0.001; OS HR 1.925, P <0.001) and
after PSM (PFS HR 1.711, P <0.001; CSS HR 2.588, P <0.001; OS HR
1.957, P <0.001).
Conclusion: The
preoperative AST/ALT ratio can be a convenient and useful prognostic biomarker
for patients with localized UTUC.
Keywords: aspartate
transaminase, alanine transaminase, upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma,
prognosis