110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

聚乙二醇化干扰素单药治疗与新型聚乙二醇干扰素加替诺福韦联合治疗慢性乙型肝炎的比较
Authors Zheng C, Yan H, Zeng J, Cai S, Wu X
Received 19 November 2018
Accepted for publication 4 March 2019
Published 12 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 845—854
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S195144
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Background and aim: We aimed
to evaluate the effectiveness of pegylated interferon (Peg-IFN) monotherapy
(IFN group) and combination therapy with tenofovir (TDF) and Peg-IFN (IFN+TDF
group) in chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients.
Patients and methods: Data of 143 CHB patients were analyzed in this study. All patients
enrolled received liver biopsy. Virologic responses were defined as hepatitis B
virus (HBV) DNA <100 IU/mL, biochemical responses were defined as
normalization of alanine aminotransferse (ALT) levels, and HBeAg
serological response was defined as
HBeAg loss or HBeAg seroconversion to HBeAb.
HBsAg serological response was defined as HBsAg loss or HBsAg
seroconversion to HBsAb.
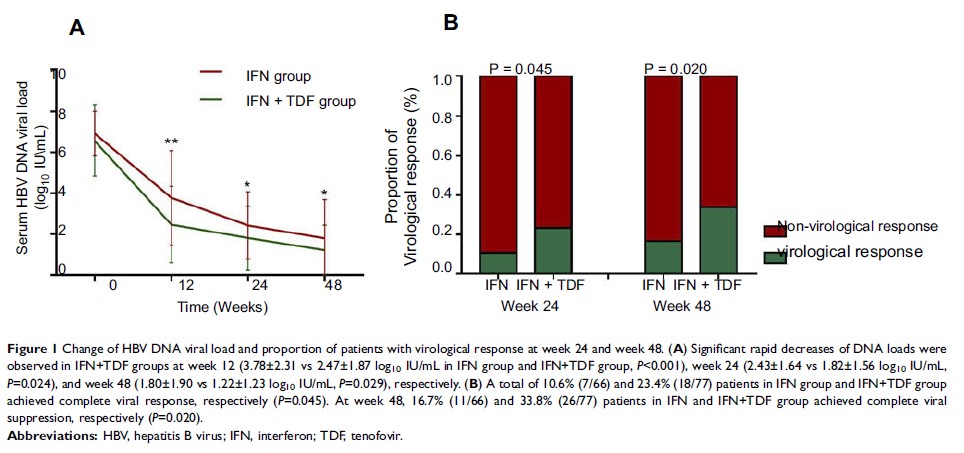
Results: We
observed that a total of 16.7% (11/66) and 33.8% (26/77) patients in IFN and
IFN+TDF group achieved complete viral suppression after 48 weeks treatment (P =0.02). Although
HBeAg levels in CHB patients in the IFN+TDF group decreased more rapidly during
the 48-week treatment, we did not observe significant differences in HBeAg
serological loss or seroconversion rates between the two groups at 24 and 48
weeks. HBsAg loss was observed in 13.0% (10/77) of CHB patients in the IFN+TDF
group at 48 weeks, compared with only 3% (2/66) patients in the IFN group (P =0.032). No
significant difference was observed in HBsAg seroconversion rate between the
two groups during 48-week treatment. The biochemical response rate was also
significantly higher in the IFN+TDF group than that in the IFN group at week 48
(P =0.015).
Multivariate logistic analysis showed that IFN+TDF treatment (OR=4.41, P =0.003), severe
baseline hepatic inflammation (OR=4.16, P <0.001), and lower baseline serum HBV DNA levels
(OR=0.98, P =0.03)
were strong predictors for the virological response. Younger age
(OR=0.89, P =0.01),
higher baseline ALT level (OR=1.01, P =0.038), and lower baseline HBeAg level
(OR=0.99, P =0.008)
were independent predictors for HBeAg sero-response after 48 weeks treatment.
While only severe liver fibrosis (OR=1.69, P =0.028) and lower
baseline HBsAg level (OR=0.22, P =0.005) were independent factors associated with HBsAg
sero-response after 48 weeks treatment.
Conclusion: Peg-IFN
combined with TDF may increase the virological response rate, biochemical
response rate, and HBsAg loss rate in patients with CHB infection. The
combination treatment is more suitable for those patients who are likely to
respond to the treatment.
Keywords: hepatitis
B, virological response, pegylated interferon, tenofovir