110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

溶瘤病毒化疗在喉鳞状细胞癌细胞和小鼠异种移植物中具有抗肿瘤作用
Authors Wang Y, Wang B, Liang J, Cui C, Ying C, Huang F, Ma B, Zhou X, Chu L
Received 28 November 2018
Accepted for publication 17 March 2019
Published 15 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3285—3294
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S196304
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
Background: Oncolytic
virus can specifically replicate in and then lyse tumor cells, but seldom in
normal cells. Further studies have shown the significant therapeutic effect of
oncolytic virotherapy combining with other strategies, such as chemo-, radio-,
and immunotherapy et al. In this study, we investigated the combinational
effect of oncolytic virus ZD55-TRAIL and chemotherapy drug doxorubicin (DOX) on
human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC).
Methods: The
effect of ZD55-TRAIL combined with DOX on cell growth was assessed in LSCC Hep2
cells and normal cells by MTT assay. Hochest 33342 staining was performed to
observe cell morphological changes. Western blot was used to detect the
expression of apoptotic activation proteins. The in vivo antitumor efficacy of
combination treatment was estimated in laryngeal cancer xenograft models.
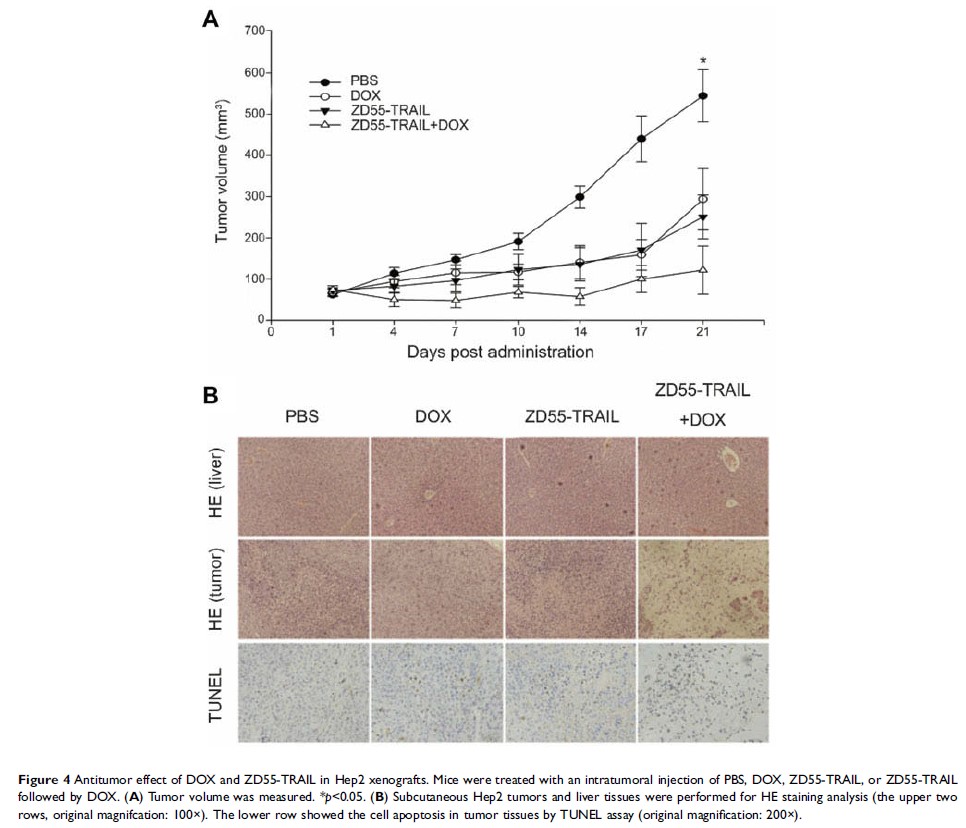
Results: The
combination of ZD55-TRAIL and DOX exhibited enhanced inhibitory effects on
laryngocarcinoma cell growth, and had few side effects to normal cells in
vitro. Chemotherapy drug increased the inducement of tumor cell apoptosis
mediated by oncolytic virus. In vivo experiment confirmed that the combination
treatment significantly inhibited Hep2 laryngocarcinoma xenografts growth in
mice.
Conclusion: The
oncolytic viro-chemotherapy is a potent therapeutic approach for in vitro
cytotoxicity evaluation of Hep2 cells and xenograft growth in vivo.
Keywords: laryngocarcinoma,
oncolytic virus, ZD55-TRAIL, doxorubicin