110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于社区的中国患者 2 型糖尿病调查所显示的脂质积聚产物与糖尿病视网膜病变之间的关系
Authors Wu J, Zhong Y, Yue S, Guan P, Zhang G, Liu L, Chen L
Received 22 November 2018
Accepted for publication 19 February 2019
Published 16 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 513—518
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S195578
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Juei-Tang Cheng
Purpose: Abnormal
levels of lipid accumulation product (LAP) have been associated with risk of
cardiovascular disease and diabetes. However, it is not clear whether LAP index
is associated with diabetic retinopathy (DR). We investigated the association
between LAP index and DR in Chinese adults with diabetes.
Patients and methods: We
included 427 Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes aged 18-year over who
participated in a community-based cross-sectional study in Shenyang. DR was
addressed on retinal photographs graded using the modified Airlie House
classification. LAP was defined as (waist circumference [cm]–65) ×
(triglycerides [mmol/L]) in men, and (waist circumference [cm]–58) ×
(triglycerides [mmol/L]) in women and analyzed continuously (per SD change) and
categorically (quartile 1, <30; quartile 2, 30–50; and quartile 3, >50).
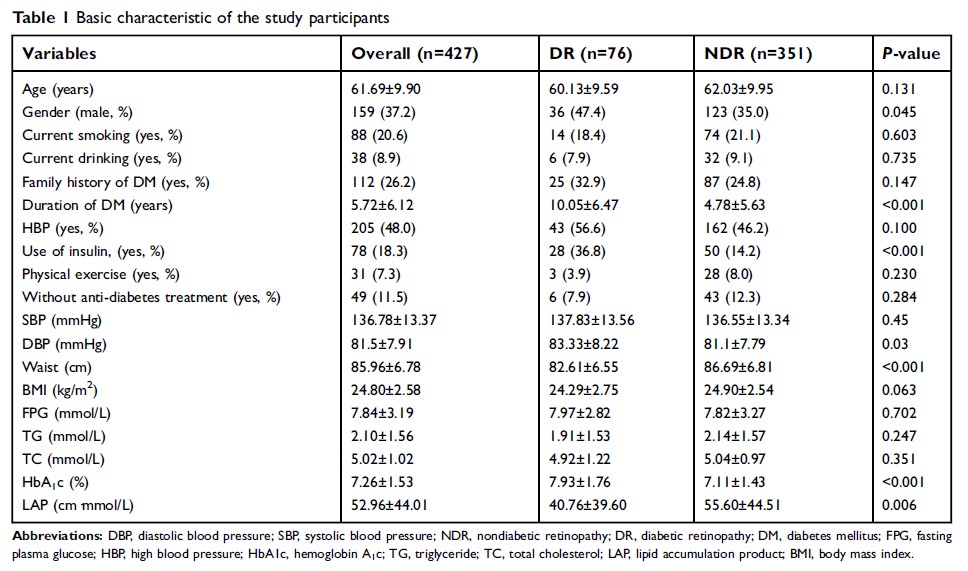
Results: Prevalence
of DR among the study population was 17.8%. The mean level of LAP was
52.96±44.01. Compared to quartile 1 level, both quartile 2 and 3 levels were
associated with DR with multivariable odds ratio (95% CI) of 0.23 (0.12–0.46)
and 0.27 (0.14–0.54), respectively. These associations persisted when LAP was
analyzed continuously (0.57 [0.35–0.92]).
Conclusion: Higher
central lipid accumulation in Chinese diabetics is related to the lower risk of
DR, suggesting that LAP may be useful for identifying type 2 diabetes mellitus
patients who are at risk for DR.
Keywords: diabetic
retinopathy, lipid accumulation product, diabetes