110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

LncRNA MIR100HG 通过下调 miR-204-5p 促进喉鳞状细胞癌中癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Huang Y, Zhang C, Zhou Y
Received 22 January 2019
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 17 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2967—2973
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S202528
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: LncRNA
MIR100HG promotes several types of malignancies, while its involvement in other
human diseases is unknown.
Patients and methods: Our study
included 70 patients with LSCC who were diagnosed and treated in the First
Affiliated Hospital and College of Clinical Medicine of Henan University of
Science and Technology from January 2016 to July 2018. qRT-PCR, cell
transfection, in vitro cell proliferation assay, cell migration and invasion
assay were applied for the research.
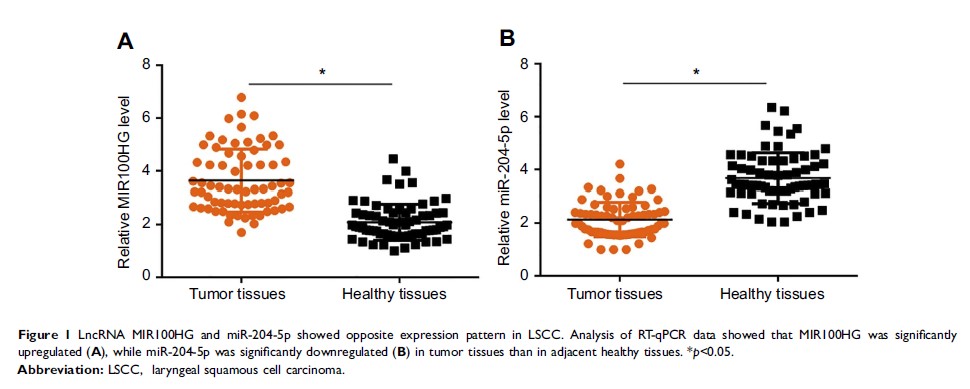
Results: In the
present study we found that MIR100HG was upregulated, while miR-204-5p was
downregulated in tumor tissues than in adjacent healthy tissues of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) patients. Expression of MIR100HG was significantly
affected by AJCC stage. A significant and inverse correlation between MIR100HG
and miR-204-5p was found in tumor tissues but not in adjacent healthy tissues
of LSCC patients. Overexpression of MIR100HG resulted in the downregulation of
miR-204-5p in LSCC cells, while miR-204-5p overexpression failed to
significantly affect MIR100HG expression. Overexpression of MIR100HG led to
promoted, while miR-204-5p, overexpression led to inhibited proliferation,
migration and invasion of LSCC cells. In addition, miR-204-5p overexpression
attenuated the enhancing effects of MIR100HG overexpression on cancer cell
proliferation, migration and invasion.
Conclusion: Therefore,
lncRNA MIR100HG promoted cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in
LSCC possibly through the downregulation of miR-204-5p.
Keywords: laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma, lncRNA MIR100HG, miR-204-5p