110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

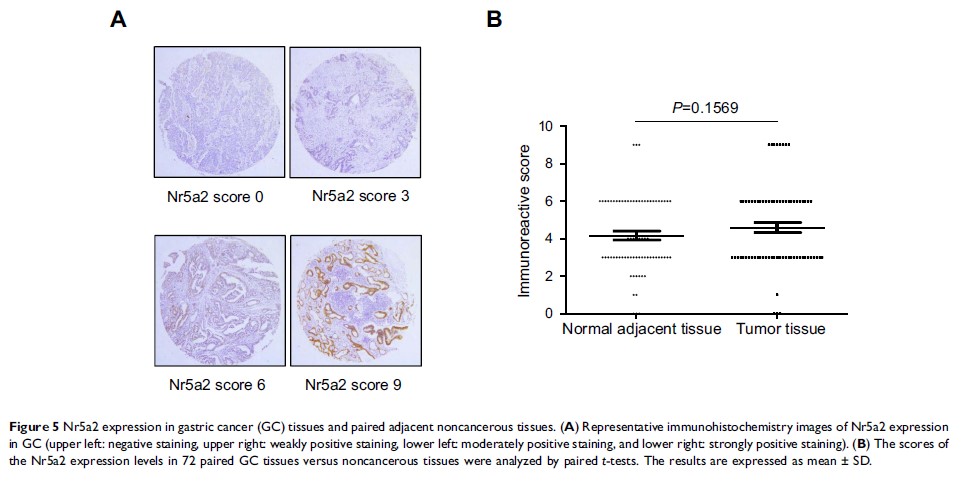
Nr5a2 通过 Wnt/β-连环蛋白信号传导促进胃癌 AGS 细胞的肿瘤生长和转移
Authors Liu L, Li Y, Pan B, Zhang T, Wei D, Zhu Y, Guo Y
Received 11 January 2019
Accepted for publication 19 March 2019
Published 17 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 2891—2902
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S201228
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: Nr5a2
(nuclear receptor subfamily 5 group A member 2, also known as LRH-1), which
belongs to the NR5A (Ftz-F1) subfamily of nuclear receptors, is a key regulator
in stem cell pluripotency and the development of several types of cancer.
However, the data are controversial. Since Nr5a2 plays different roles in
multiple types of cancer and the function of Nr5a2 in gastric cancer (GC) has
not been revealed, we studied the role and molecular mechanism of Nr5a2 in GC.
Methods: In this
study, we have investigated the effect of Nr5a2 on tumor growth and metastasis
by in vivo and in vitro models.
Results: The
results showed that knockdown of Nr5a2 could inhibit cell proliferation via
arresting the cell cycle in the G2/M phase and suppress cell mobility through
preventing the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process in AGS cells. In
addition, knockdown of Nr5a2 could suppress tumorigenesis and metastasis of AGS
cells in vivo. We also demonstrated that knockdown of Nr5a2 inhibited cellular
proliferation and mobility by suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling
pathway.
Conclusion: Nr5a2 may
act as an oncogene in GC development. The EMT process and the Wnt/beta-catenin
signaling pathway play an important role in the Nr5a2 induced GC development.
Keywords: Nr5a2,
gastric cancer, proliferation, metastasis, Wnt/beta-catenin