110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

SMARCE1 的高表达预示着预后不良并促进胃癌中的细胞生长和转移
Authors Liu H, Zhao YR, Chen B, Ge Z, Huang JS
Received 19 November 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 23 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3493—3509
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S195137
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Background: Gastric
cancer (GC) is one of the most lethal cancers worldwide with a high risk for
recurrence and metastasis. Therefore, further understanding of the metastatic
mechanism and the development of treatment strategies are required. Although
increasing evidence suggests that SWI/SNF Related, Matrix Associated, Actin
Dependent Regulator of Chromatin, Subfamily E, Member 1 (SMARCE1) promotes
cancer metastasis, its role in GC remains unclear.
Materials and methods: GC
samples (n=122) were used to investigate the association between SMARCE1
expression, patient clinicopathological features, and prognosis. The expression
of SMARCE1 in GC tissues was measured using real-time polymerase chain
reaction, western blotting, and immunohistochemistry. MGC-803 and AGS cells were
transfected with lentivirus to upregulate or downregulate SMARCE1 expression.
The roles of SMARCE1 in GC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion were
determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 assay, colony formation assay, wound
healing, transwell migration, and invasion assay. Nude mice models were
established to observe tumorigenesis. The specific mitogen-activated protein
kinase (MAPK) inhibitor U0126 was utilized to verify the involved pathway.
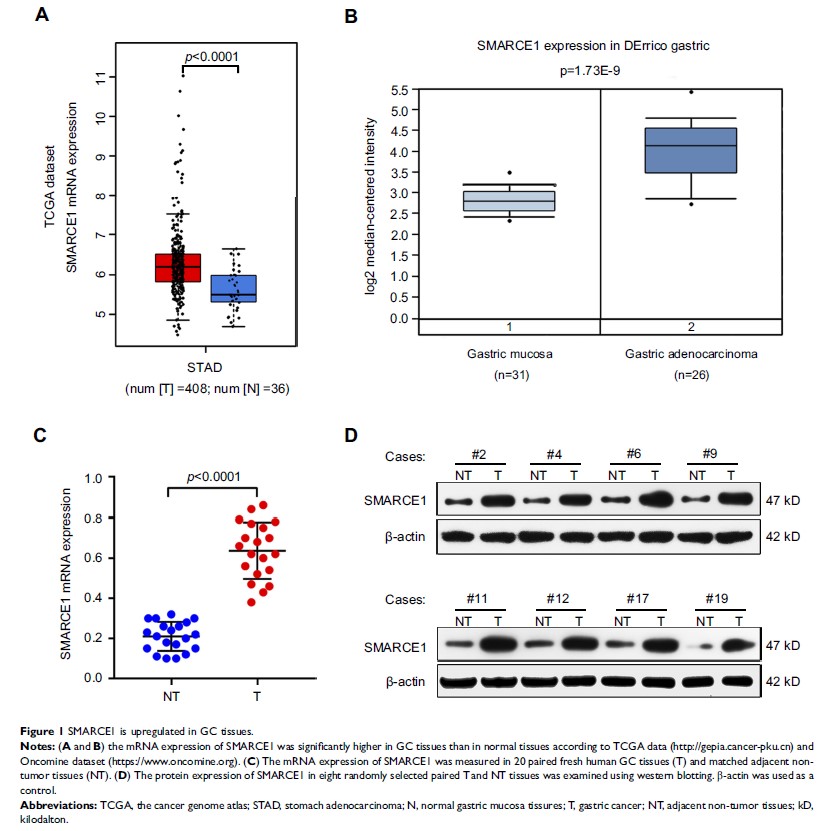
Results: SMARCE1
was highly expressed in GC tissues and cell lines. High expression of SMARCE1
was correlated with the malignant clinicopathological characteristics of GC
patients, including tumor size, depth of invasion, degree of differentiation,
lymph node involvement, and TNM stage (all P <0.05).
Kaplan–Meier survival analysis revealed that high SMARCE1 expression predicted
poor prognosis in GC patients (P <0.01). Moreover, SMARCE1 was an independent risk
factor of poor prognosis (P <0.01). Functional study revealed that
overexpression of SMARCE1 markedly promoted the proliferation, migration, and
invasion of GC cells in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo. Furthermore, SMARCE1
activated the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway. U0126 significantly inhibited the
SMARCE1-induced proliferation and mobility of GC cells.
Conclusion: SMARCE1
promoted growth and metastasis of GC, indicating its potential usefulness as a
prognostic biomarker and target for therapeutic intervention against this
disease.
Keywords: SMARCE1,
gastric cancer, prognosis, proliferation, metastasis