110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

大鼠脊髓中 lncRNA Malat1 的表达下降通过增加臂丛神经撕脱后的神经元兴奋性而导致神经性疼痛
Authors Meng C, Yang X, Liu Y, Zhou Y, Rui J, Li S, Xu C, Zhuang Y, Lao J, Zhao X
Received 18 November 2018
Accepted for publication 15 March 2019
Published 23 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1297—1310
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S195117
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael Ueberall
Purpose: Neuropathic
pain (NP) is a challenging clinical problem due to its complex pathogenesis. In
our previous study using microarray, we found that the levels of lncRNA Malat1
were decreased in the spinal cord of NP rat after brachial plexus avulsion, but
its contribution to NP remain unclear. The purpose of this study was to
investigate its role in the pathogenesis of NP.
Methods: In the NP
model of complete brachial plexus avulsion rat, spinal cords were harvested,
and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was used to test the spatial
expression of Malat1 and qRT-PCR was used to confirm the quantitative
expression of Malat1. In primary cultured neurons, Malat1 expression interfered
with adenovirus. Spontaneous electric activities of neurons were tested using
multi-electrode arrays and apoptosis of neurons was tested using TUNEL method.
The change of intracellular calcium concentration was analyzed using calcium
imaging method.
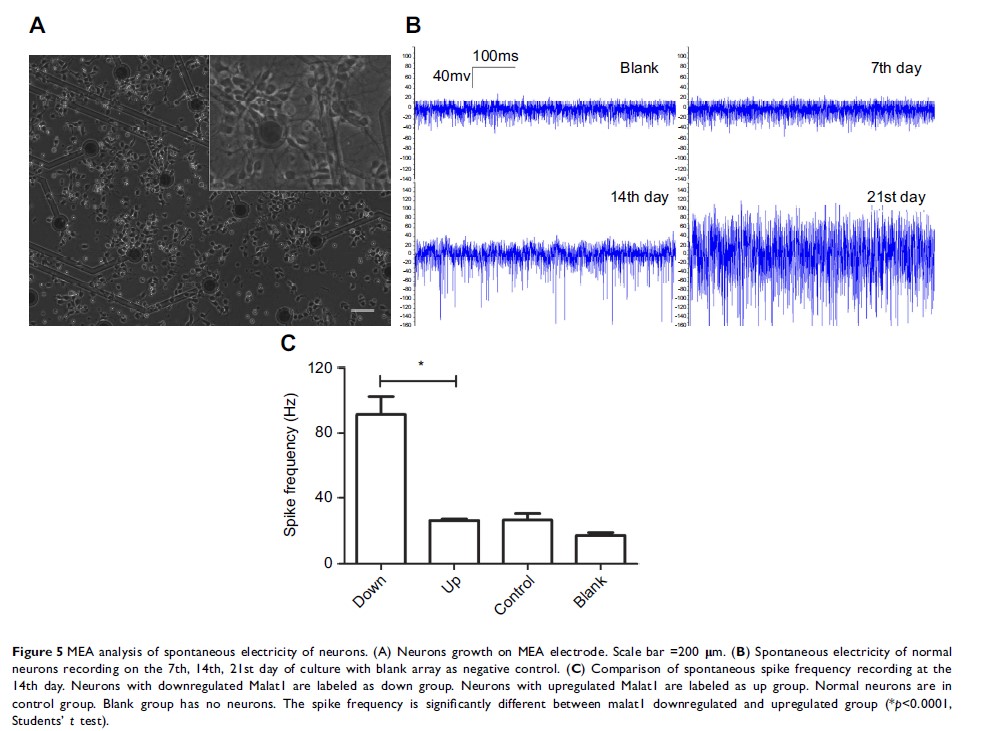
Results: Decreased
Malat1 expression was confirmed using qRT-PCR, and Malat1 was identified in the
cytoplasm of neurons in spinal cord, but not in glia. In vitro, the decrease of
Malat1 resulted in an increase in the frequency of spontaneous electric
activity in neurons but had no effect on neuronal apoptosis. Further analysis indicated
during glutamate stimulation, the change of intracellular calcium concentration
in neurons with downregulated Malat1 expression was significantly greater than
that in normal neurons.
Conclusion: Reduced
Malat1 expression may induce NP by increasing neuronal excitability in the
spinal cord via regulation of calcium flux.
Keywords: neuropathic
pain, lncRNA, Malat1, spinal cord, neuron, multielectrode array, brachial
plexus avulsion