110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

电针通过 μ 阿片受体的作用来减少 Netrin-1 诱导的有髓传入纤维发芽和神经性疼痛
Authors Li HP, Su W, Shu Y, Yuan XC, Lin LX, Hou TF, Xiang HC, Zhu H, Hu XF, Pan L, Wu JN, Meng XF, Pan HL, Wu CH, Li M
Received 25 October 2018
Accepted for publication 21 February 2019
Published 23 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1259—1268
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S191900
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Michael E Schatman
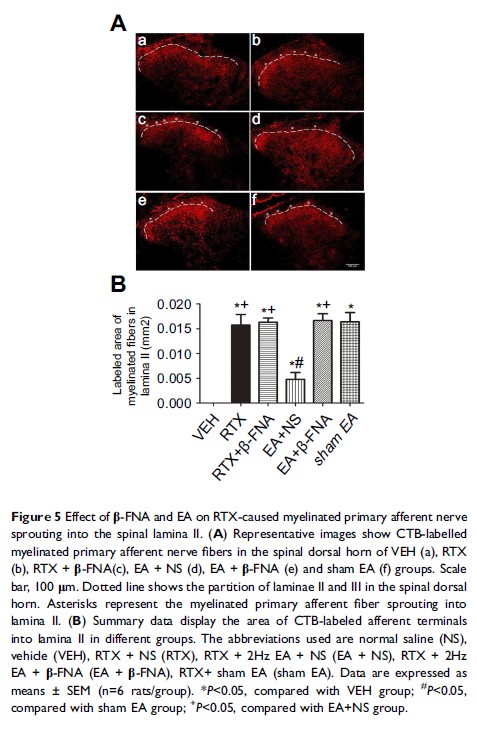
Purpose: We
determined whether electroacupuncture (EA) reduces Netrin-1-induced myelinated
primary afferent nerve fiber sprouting in the spinal cord and pain
hypersensitivity associated with postherpetic neuralgia (PHN) through
activation of μ-opioid receptors.
Methods: PHN was
induced by systemic injection of resiniferatoxin (RTX) in rats. Thirty-six days
after RTX injection, a μ-opioid receptor antagonist, beta-funaltrexamine
(β-FNA) or a κ-opioid receptor antagonist, nor Binaltorphimine (nor-BNI), was
injected intrathecally 30 mins before EA, once every other day for
4 times. Mechanical allodynia was tested with von Frey filaments. The
protein expression level of Netrin-1 and its receptors (DCC and UNC5H2) were
quantified by using western blotting. The myelinated primary afferent nerve
fiber sprouting was mapped with the transganglionic tracer cholera toxin
B-subunit (CTB).
Results: Treatment
with 2 Hz EA at “Huantiao” (GB30) and “Yanglingquan” (GB34) decreased the
mechanical allodynia at 22 days and the myelinated primary afferent nerve
fiber preternatural sprouting into the lamina II of the spinal dorsal horn at
42 days after RTX injection. Also, treatment with 2 Hz EA reduced the
protein levels of DCC and Netrin-1 and promoted the expression of UNC5H2 in the
spinal dorsal horn 42 days after RTX injection. Furthermore, the μ-opioid
receptor antagonist β-FNA, but not the κ-opioid receptor antagonist nor-BNI,
reversed the effect of EA on neuropathic pain caused by RTX. In addition,
morphine inhibited the Netrin-1 protein level induced by RTX in SH-SY5Y cells.
Conclusions: Through
activation of μ-opioid receptors, treatment with EA reduces the expression
level of DCC and Netrin-1 and changes a growth-permissive environment in spinal
dorsal horn into an inhibitory environment by increasing UNC5H2, thus
decreasing RTX-caused primary afferent nerve sprouting in the spinal dorsal
horn and neuropathic pain.
Keywords: postherpetic
neuralgia, analgesia, mechanical hyperalgesia, rat, μ-opioid receptors