110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

白花丹素通过下调 SIVA 的表达抑制肝细胞癌的增殖并诱导其凋亡
Authors Li T, Lv M, Chen X, Yu Y, Zang G, Tang Z
Received 8 January 2019
Accepted for publication 6 March 2019
Published 23 April 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1289—1300
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S200610
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Jianbo Sun
Purpose: Plumbagin is thought to be a bioactive
phytochemical drug and exerts an antitumor effect on various cancers. However,
few studies focus on the antitumor activity of plumbagin on liver cancer. This
study first investigated the antitumor activity of plumbagin on liver cancer
and further investigated the molecular mechanism of its antitumor activity
against hepatocellular carcinoma, both in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: The
antiproliferative activity of plumbagin was evaluated through CCK-8, EdU, and
colony forming test. The cell cycle and apoptosis were then analyzed by flow
cytometer. Western blot was used to detect the expression of apoptosis related
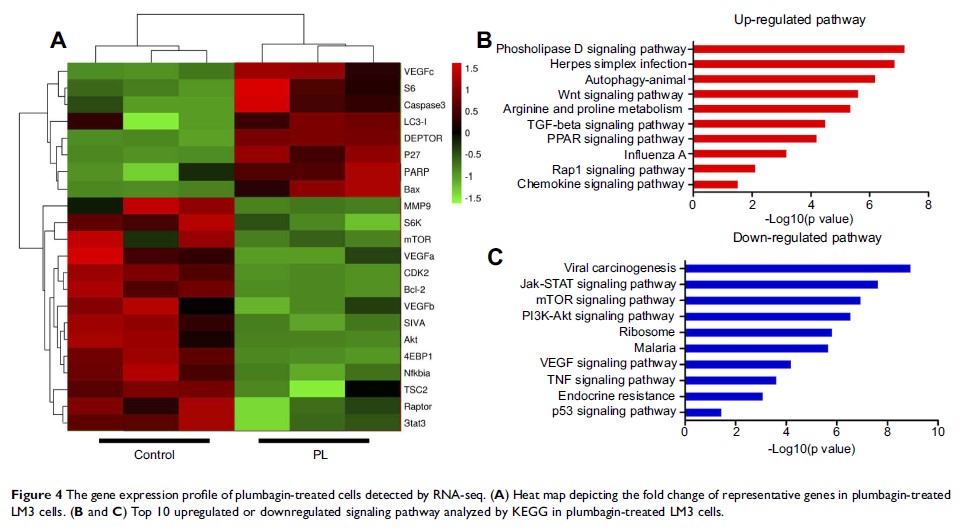
protein, SIVA, and mTOR pathway. RNA-seq was performed to determine the gene
expression profiles and overexpressed or knocked down SIVA to validate its role
in plumbagin’s antitumor activity. Regarding animal experiment, a xenograft
model in BALB/c nude mice was built using LM3-Luci cells. Then bioluminescence
imaging and further immunohistochemistry were performed to study the antitumor
activity and the expression of SIVA and mTOR in the plumbagin-treated group.
Results: Plumbagin
can inhibit proliferation and induce apoptosis of liver cancer cells in vitro.
Further experiment demonstrated that plumbagin could inhibit the expression of
SIVA and subsequently downregulate the mTOR signaling pathway, and upregulating
the expression of SIVA will alleviate the antitumor activity of plumbagin on
liver cancer, which confirmed the important role of the SIVA/mTOR signaling
pathway in the antitumor activity of plumbagin. In vivo bioluminescence imaging
showed a decreased signal in the plumbagin-treated group, and further
immunohistochemistry demonstrated that plumbagin could inhibit the SIVA/mTOR
signaling pathway in tumor tissues.
Conclusion: Our
promising results showed that plumbagin could inhibit proliferation and induce
apoptosis of hepatic cancer through inhibiting the SIVA/mTOR signaling pathway
for the first time, which indicated that plumbagin might be a good candidate
against liver cancer.
Keywords: hepatocellular
carcinoma, plumbagin, antitumor, apoptosis, SIVA, mTOR