110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

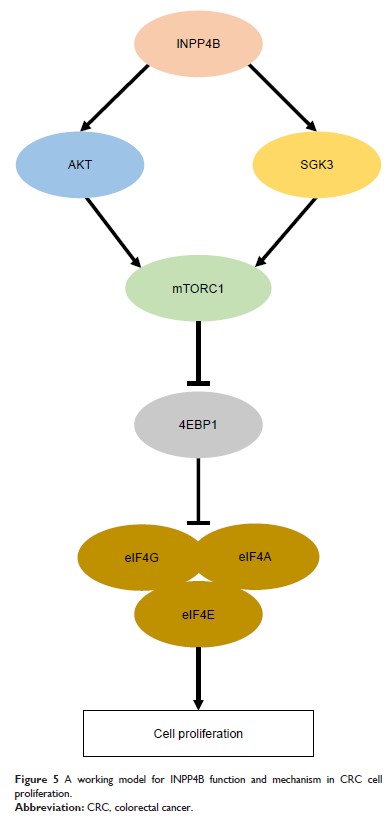
INPP4B 通过激活 mTORC1 信号传导和帽依赖性翻译来促进结肠直肠癌细胞增殖
Authors Ruan X, Liu X, Yang Z, Zhang S, Li Q, Lin C
Received 4 September 2018
Accepted for publication 6 February 2019
Published 23 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3109—3117
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S186365
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr XuYu Yang
Background and objective: Inositol
polyphosphate 4-phosphatase type II (INPP4B) is overexpressed in CRC tissues,
and emerges as an oncogene. However, the mechanism by which INPP4B regulates
CRC cell proliferation remains largely unclear. In this study, we aimed to
investigate the regulatory mechanisms of INPP4B in CRC.
Materials and methods: The
expression levels of mRNA were detected by qRT-PCR. The expression levels
of protein were determined by Western blot. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays
and BrdU incorporation assays were performed to evaluate cell proliferation
abilities. Bicistronic luciferase assays and the m7GTP pull down assay were
performed to measure the cap-dependent translation in cells.
Results: INPP4B
promotes CRC cell proliferation by increasing mTORC1 activity. Furthermore, it
was shown that the activation of mTORC1 signaling by INPP4B led to increased
cap-dependent translation, which is essential for INPP4B-mediated CRC cell
proliferation. Finally, it was demonstrated that increased AKT and serum and
glucocorticoid-inducible kinase 1 activity contributed to the activation of
cap-dependent translation induced by INPP4B.
Conclusion: Collectively,
the present study reveals INPP4B promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation
by activating mTORC1 signaling and cap-dependent translation.
Keywords: colorectal
cancer, INPP4B, mTORC1, 4E-BP1, cap-dependent translation