110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CHPF 的敲除可抑制非小细胞肺癌的细胞进展
Authors Hou XM, Baloch Z, Zheng ZH, Zhang WH, Feng Y, Li DD, Wu XA, Yang SH
Received 24 October 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 24 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3275—3283
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S192036
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Purpose: The aim
of the present study was to explore the role of CHPF in non-small-cell lung
cancer (NSCLC) and to develop an shRNA vector-based therapy to repress the
expression of CHPF gene in NSCLC cell lines.
Methods: In this
study, we used immunohistochemical staining to verify the expression of CHPF in
NSCLC tissue. Then, we determined the expression of CHPF gene in different
NSCLC cell lines with RT-PCR and Western blotting. Specific CHPF shRNA was used
to knockdown the expression of CHPF. Celigo image cytometry, cell cycle
analysis, and flow cytometry assay were performed.
Results: The
results showed that expression level of CHPF was higher in NSCLC tissues than
normal lung tissues. Further, we established that CHPF expression knockdown in
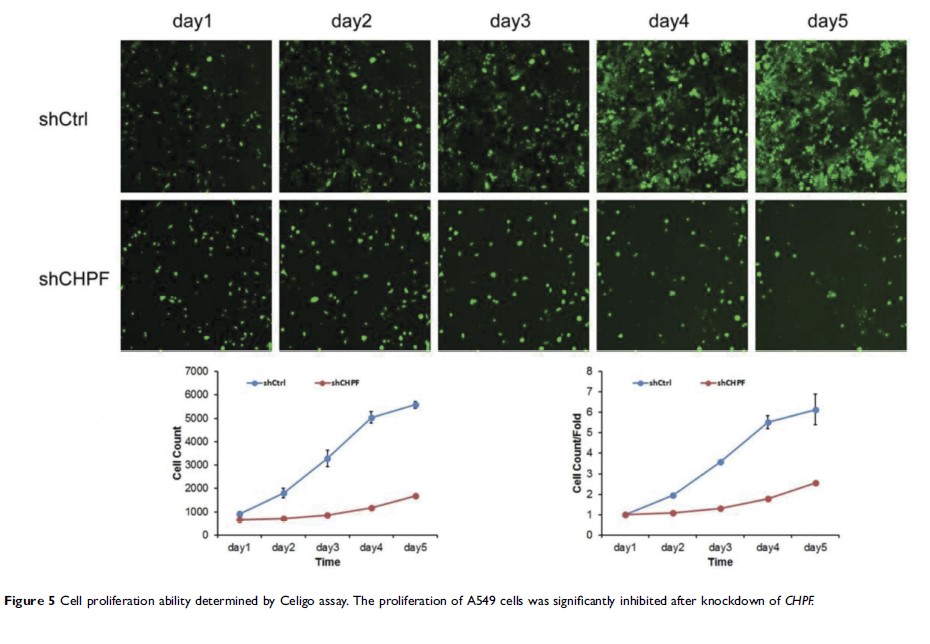
NSCLC cells could substantially restrain the cell proliferation, apoptosis, and
cell cycle in vitro.
Conclusion: On the
basis of these results, we concluded that CHPF expression has an important role
in the progression of human NSCLC cells. Therefore, its interference could
possibly be used as a potential therapeutic target against NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC,
CHPF, progression, knockdown