110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

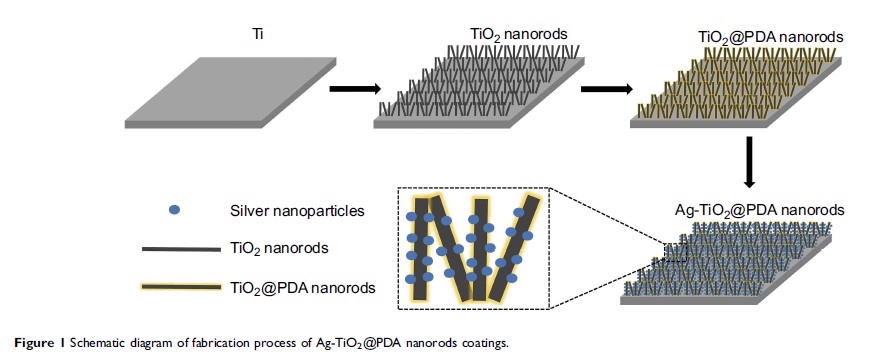
通过选择性物理穿刺和聚多巴胺可控的离子释放,以及载有银纳米颗粒的 TiO2 纳米棒所实现的体外和体内长效杀菌活性
Authors Guan M, Chen Y, Wei Y, Song H, Gao C, Cheng H, Li Y, Huo K, Fu J, Xiong W
Received 23 January 2019
Accepted for publication 3 April 2019
Published 24 April 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 2903—2914
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S202625
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Titanium
(Ti) implant-associated infection, which is mostly caused by bacterial adhesion
and biofilm formation, may result in implant failure and secondary surgery.
Thus it is an urgent issue to prevent bacterial infections at the earliest
step.
Purpose: To
develop a novel surface strategy of polydopamine (PDA) and silver (Ag)
nanoparticle-loaded TiO2 nanorods (NRDs) coatings on Ti alloy.
Materials and methods: Ag-TiO2@PDA NRDs was
fabricated on Ti alloy by hydrothermal synthesis. The antibacterial activity of
Ag-TiO2@PDA NRDs against Escherichia coli and
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus were tested by FE-SEM,
Live/Dead staining, zone of inhibition, bacteria counting method and protein
leakage analysis in vitro . In addition, an implant infection model was
conducted and the samples were tested by X-ray, Micro-CT and histological
analysis in
vivo . Besides, cell morphology and cytotoxicity of Mouse calvarial
cells (MC3T3-E1) were characterized by FE-SEM, immunofluorescence and CCK-8
test in
vitro .
Results: Our study
successfully developed a new surface coating of Ag-TiO2@PDA NRDs. The
selective physical puncture of bacteria and controlled release of Ag+ ions of
Ag-TiO2@PDA NRDs achieved a long-lasting bactericidal
ability and anti-biofilm activity with satisfied biocompatibility.
Conclusion: This
strategy may be promising for clinical applications to reduce the occurrence of
infection in the implant surgeries
Keywords: bacterial
infection, polydopamine, silver nanoparticles, physical puncture, TiO2 nanorods,
bactericidal activity