110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

MiR-155-5p 通过靶向 TP53INP1 加速宫颈癌细胞的转移
Authors Li N, Cui T, Guo WL, Wang DW, Mao L
Received 1 November 2018
Accepted for publication 13 March 2019
Published 29 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3181—3196
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S193097
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Arseniy Yuzhalin
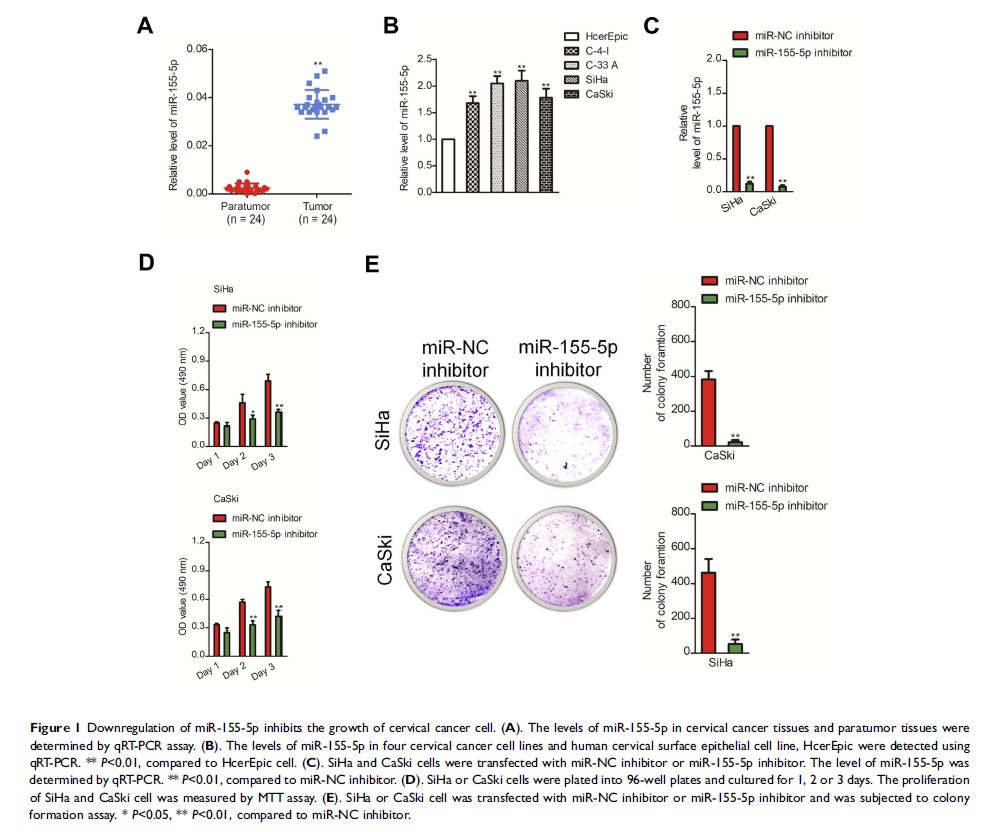
Background: The
dysregulation of microRNAs has been implicated in the progression of different
malignancies. Herein, we sought to identify the precise roles of miR-155-5p in
the progression of cervical cancer.
Materials and methods: The
expressions of miR-155-5p in cervical carcinoma cells and clinical tissues were
assessed using qRT-PCR analysis. The functions of miR-155-5p on the growth of
cervical cancer cell were investigated using MTT and colony formation. The
Transwell and wound closure assays were selected to explore the influence of
miR-155-5p on the invasion and migration of cervical cancer cell. The effect of
miR-155-5p on cervical carcinoma cell growth and metastasis in vivo was
investigated using xenograft model and experimental lung metastasis model.
Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay were applied to identify
that tumor protein p53-inducible nuclear protein 1 (TP53INP1) was the target of
miR-155-5p.
Results: MiR-155-5p
was significantly upregulated in cervical cancer tissue than that in control
normal tissue. Downexpression of miR-155-5p decreased the growth, migration as
well as invasiveness abilities of cervical cancer cell in vitro whereas
overregulation of miR-155-5p caused the opposite outcomes. In addition, the in
vivo mice xenograft model suggested that downexpression of miR-155-5p
restrained the progression of cervical cancer cell whereas overexpression of
miR-155-5p caused opposite outcomes. Furthermore, we revealed that TP53INP1 was
the target of miR-155-5p and the level of TP53INP1 was inversely associated
with miR-155-5p level in cervical carcinoma. Furthermore, TP53INP1 knockdown
mimicked the influence of miR-155-5p on cervical cancer proliferation,
migration and invasion phenotypes. Finally, overexpression of TP53INP1 impaired
the promote effect of miR-155-5p on cervical cancer cell and downregulation of
TP53INP1 counteracted the suppressive impact of miR-155-5p on the
aggressiveness of cervical cancer cell.
Conclusion: Our study
indicated that miR-155-5p regulated the development of cervical cancer cell by
regulating the expression of TP53INP1.
Keywords: miR-155-5p,
cervical cancer, TP53INP1, metastasis