110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

CLDN8 通过激活 MAPK/ERK 信号传导促进结肠直肠癌细胞增殖、迁移和侵袭
Authors Cheng B, Rong A, Zhou Q, Li W
Received 3 October 2018
Accepted for publication 10 December 2018
Published 30 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3741—3751
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S189558
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Antonella D'Anneo
Background: Claudin 8
(CLDN8), an integral membrane protein that constitutes tight junctions in cell
membranes, was recently implicated in tumor progression. However, its roles in
colorectal cancer (CRC) progression and metastasis remain unknown.
Methods: In this
study, we examined the effect of CLDN8 on the progression of CRC, including
cell proliferation, migration, and invasion, and determines its underlying
molecular mechanism using in vitro CRC cell lines and in vivo mouse xenograft
models.
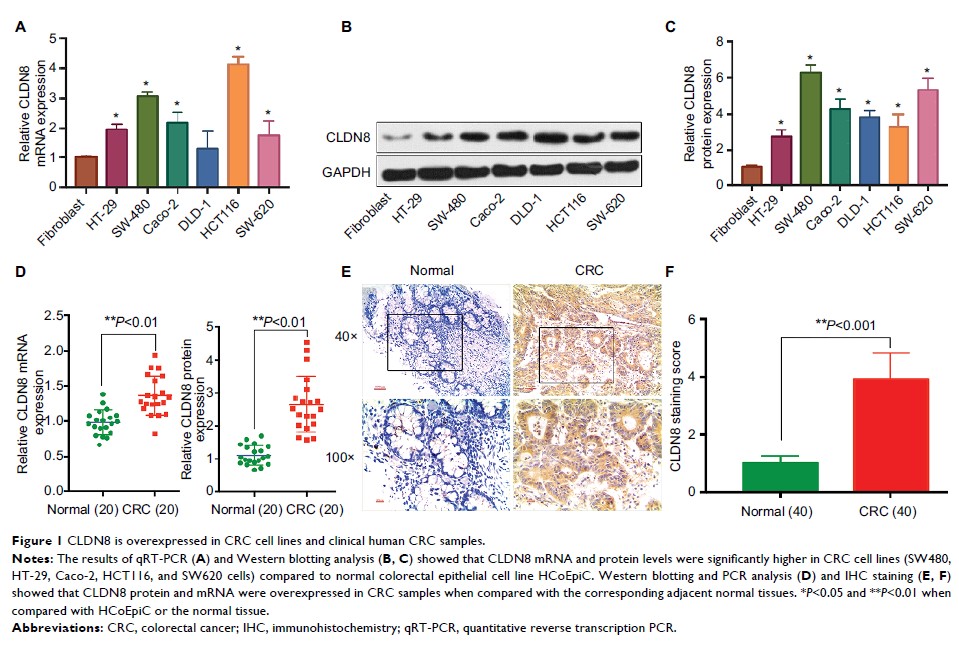
Results: We found
that CLDN8 expression in human CRC tissues was significantly higher than that
in adjacent normal tissues. The knockdown of CLDN8 markedly suppressed the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of SW480 and HT-29 CRC cells, whereas
the overexpression of CLDN8 notably promoted tumor progression in SW480 and
HT-29 CRC cells. Mechanistic studies revealed that CLDN8 upregulated p-ERK
(p-PKB/AKT) and MMP9 in CRC cells. Notably, the MAPK/ERK inhibitor PD98095
dramatically attenuated the effects of CLDN8 on p-ERK and MMP9. Moreover,
PD98095 remarkably blocked the tumor-promoting activity of CLDN8. The knockdown
of CLDN8 also inhibited the in vivo tumor growth in a nude mouse xenograft
model. Collectively, CLDN8 promoted CRC cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion, at least in part, by activating the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.
Conclusion: These
findings suggest that CLDN8 exhibits an oncogenic effect in human CRC
progression.
Keywords: CLDN8,
colorectal cancer, MAPK/ERK signalling