110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

lncRNA CADM1-AS1 抑制肝细胞癌中 PTEN/AKT/GSK-3β 轴的细胞周期进程和侵袭
Authors Wang F, Qi X, Li Z, Jin S, Xie Y, Zhong H
Received 10 December 2018
Accepted for publication 24 March 2019
Published 30 April 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 3813—3828
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S197673
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Ahmet Emre Eskazan
Purpose: CADM1-AS1
(cell adhesion molecule 1 antisense RNA 1, long non-coding RNA), was firstly
characterized in renal clear cell carcinoma, and exhibits a tumor suppressor
role. However, its clinical relevance and exact effects in hepatocellular
carcinoma (HCC) remain unknown. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to assess
the clinical significance and function of CADM1-AS1 in HCC.
Methods: We
detected CADM1-AS1 expression in liver cancer tissue samples and cell lines,
and analyzed the association between CADM1-AS1 expression and clinical
parameters in 90 liver cancer patients. Moreover, we conducted gain-of-function
and loss-of-function studies in liver cancer cell to explore the biological
function and molecular mechanism of CADM1-AS1.
Results: CADM1-AS1
expression was reduced in HCC. Clinical data showed that this downregulation
was associated with advanced tumor stage, high TNM stage and reduced survival
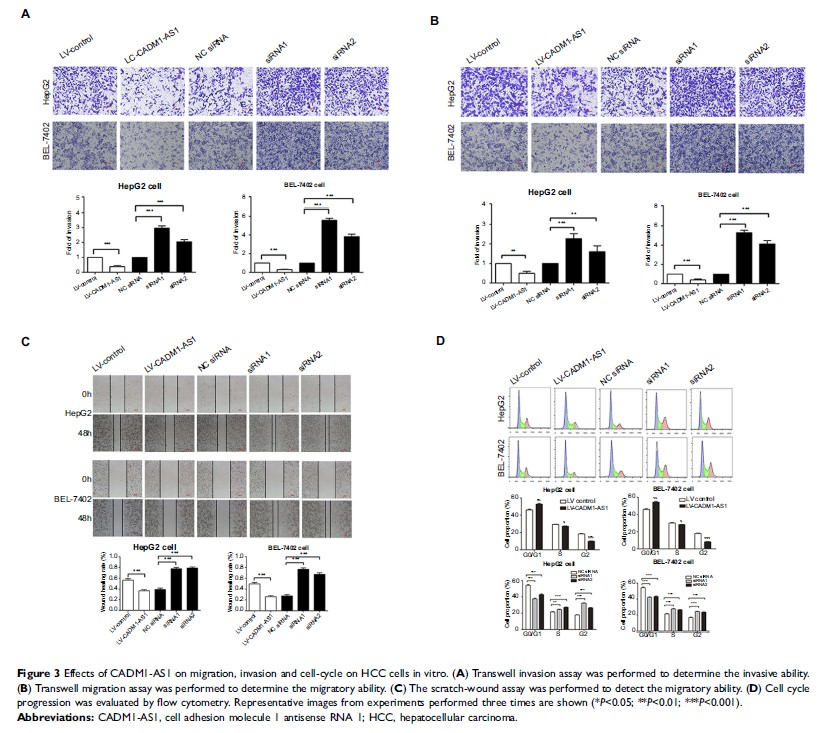
in HCC patients. CADM1-AS1 overexpression inhibited HCC cells proliferation,
migration and invasion, while inducing G0/G1 phase arrest. Meanwhile, we
revealed that CADM1-AS1 inhibited the phosphorylation of AKT and GSK-3β.
Furthermore, our study showed that CADM1-AS1 decreased the cell cycle
associated proteins expression of cyclinD, cyclinE, CDK2 CDK4, CDK6, and
enhanced the levels of p15, p21 and p27. More importantly, SC79, a specific
activator for AKT;, apparently attenuated the effects of CADM1-AS1 on above
cell-cycle associated proteins, confirming that CADM1-AS1 inhibited cell cycles
through the AKT signaling pathway. And we also found the CADM1-AS1 has
antitumor effect in vivo by a xenograft HCC mouse model. In conclusion, the
present findings show that the CADM1-AS1 inhibits proliferation of HCC by
inhibiting AKT/GSK-3β signaling pathway, then upregulate p15, p21, p27
expression and downregulate cyclin, CDK expression to inhibit the G0/G1 to S
phase transition both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion: CADM1-AS1
functions as a tumor-suppressive lncRNA. This study reveals a molecular pathway
involving PTEN/AKT/GSK-3β which regulates HCC cell-cycle progression.
Keywords: long
non-coding RNA, CADM1-AS1, proliferation, cell cycle, AKT/GSK-3β,
hepatocellular carcinoma