110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

核糖核苷酸还原酶亚基 M2 作为透明细胞肾细胞癌的新靶标
Authors Zou Y, Zhou J, Xu B, Li W, Wang Z
Received 28 November 2018
Accepted for publication 6 March 2019
Published 30 April 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3267—3275
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S196347
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
Background: Sufficient
supply of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) is required for the
uncontrolled replication of cancers. The current study aimed to investigate the
biological and clinical role of ribonucleotide reductase subunit M2 (RRM2), a
key enzyme regulating the dNTP pool, in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma
(ccRCC).
Methods: The
expression of RRM2 on disease progression and patient outcome was assessed in
ccRCC. Then, the effect of RRM2 inhibition on renal cell carcinoma (RCC) growth
using siRNA or Triapine, an RRM2-specific inhibitor, was characterized in RCC
cell lines.
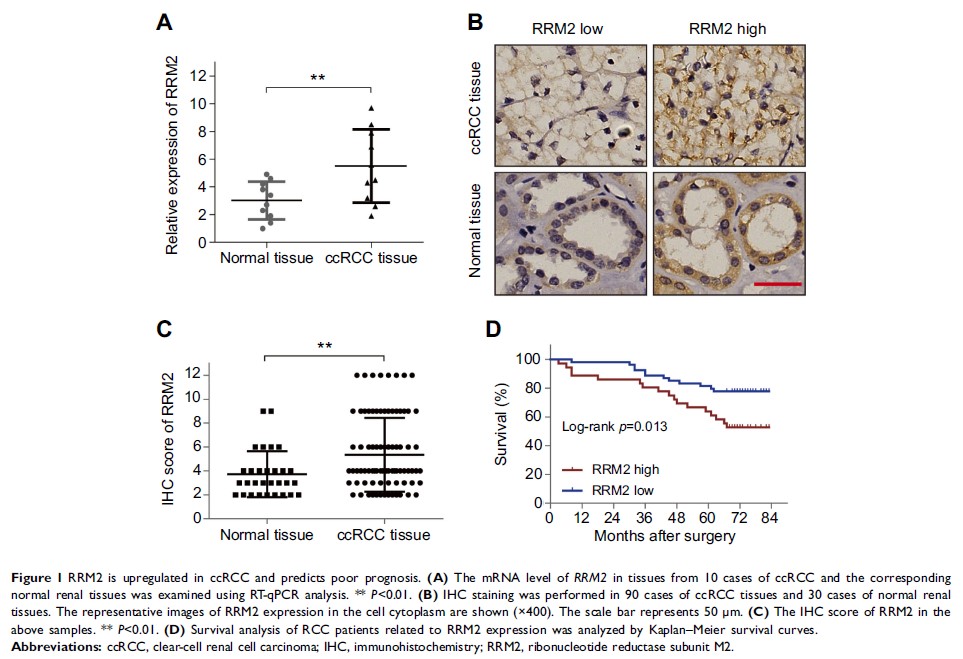
Results: The
expression of RRM2 was up-regulated in ccRCC tissues as compared to the normal
tissues. Patients with high RRM2 expression tend to have advanced pT stages,
high Fuhrman grades, and shortened overall survival (OS). RRM2-siRNAs or
Triapine significantly inhibited the cell growth by inducing G0/G1 cell cycle
arrest in RCC cells through the attenuation of dNTP pool.
Conclusions: The
current results provided evidence that RRM2 might act as a novel target for
ccRCC, and exploration of nonnucleoside, reversible, small-molecule inhibitors
against RRM2 could be promising.
Keywords: clear-cell
renal cell carcinoma, RRM2, targeted therapy