110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国晚期非小细胞肺癌患者逆转录聚合酶链反应检测细胞学标本检测 ROS1 融合的可行性
Authors Zhang L, Wang Y, Zhao C, Shi J, Zhao S, Liu X, Jia Y, Zhu T, Jiang T, Li X, Zhou C
Received 19 December 2018
Accepted for publication 1 March 2019
Published 1 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3305—3311
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S198827
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
Purpose: Our
previous study demonstrated that cytological specimens can be used as
alternative samples for detecting anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK ) fusion with
the method of reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) in patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The current study aimed to investigate the
feasibility of cytological specimens for ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor
tyrosine kinase (ROS1 ) fusion detection by RT-PCR in advanced NSCLC
patients.
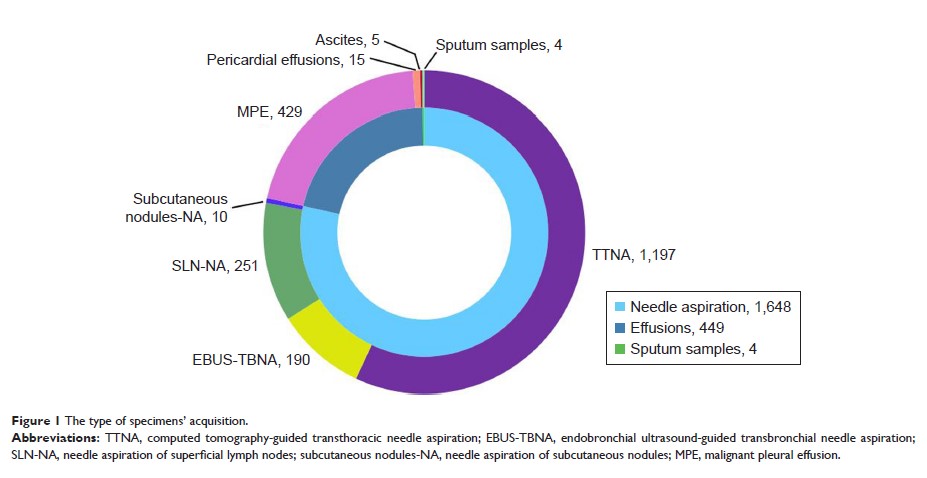
Patients and methods: A total
of 2,538 patients with advanced NSCLC, including 2,101 patients with
cytological specimens and 437 patients with tumor tissues, were included in
this study. All patients were screened for ROS1 fusion
status by RT-PCR. The efficacy of crizotinib treatment was evaluated in ROS1 fusion-positive
NSCLC patients.
Results: Among
2,101 patients with cytological specimens, the average concentration of RNA
acquired from cytological specimens was 47.68 ng/µL (95% CI, 43.24–52.62),
which was lower than the average of 66.54 ng/µL (95% CI,
57.18–76.60, P =0.001) obtained from 437 tumor tissues. Fifty-five
patients harbored ROS1 fusion gene that was detected by RT-PCR, and
14 of them were treated with crizotinib. The incidence of ROS1 fusion
was 1.95% (41/2,101) in 2,101 patients with cytological specimens, similar to
the rate of 3.20% (14/437, P =0.102) for the 437 patients with tumor tissue.
Regarding crizotinib treatment, no statistically significant differences were
observed in the objective response rate (ORR) (81.8% vs 100%, P =0.604) between
the cytological and tissue subgroups of ROS1 -positive patients.
Conclusion: This
study shows that cytological specimens can be utilized as alternative samples
for ROS1 fusion
detection by RT-PCR in advanced NSCLC patients.
Keywords: non-small-cell
lung cancer, ROS proto-oncogene 1 receptor tyrosine kinase, ROS1 , cytological
specimens, reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction, RT-PCR, crizotinib