110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

本文章已被撤回:MicroRNA-143-3p 通过靶向结肠直肠癌中的 catenin-δ1 来抑制肿瘤发生
Authors Ding X, Du J, Mao K, Wang X, Ding Y, Wang F
Received 15 August 2018
Accepted for publication 15 November 2018
Published 1 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3255—3265
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S184118
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr William Cho
***本文章已被撤回***
Background: Colorectal
cancer (CRC) is the third most common malignancy in the United States. Mounting
microRNAs (miRNAs) have been identified as oncogenes or tumor suppressors in
various cancers including CRC.
Materials and methods: The
levels of microRNA-143-3p (miR-143-3p) and catenin-δ1 (CTNND1) were determined
by RT-qPCR assay. Cell proliferative ability was assessed by Cell Counting
Kit-8 assay. Cell migratory and invasive capacities were measured by transwell
migration and invasion assay. Luciferase reporter assay was conducted to
explore whether miR-143-3p could bind with CTNND1 3'UTR. CTNND1 protein level
was determined through Western blot assay. Mouse xenograft models of CRC were
established to test the functions and molecular basis of miR-143-3p in the
development of CRC in vivo.
Results: Low
amounts of miR-143-3p were expressed in CRC tissues and cells. Functional
analysis revealed that miR-143-3p overexpression suppressed cell proliferation,
migration and invasion in CRC. Molecular mechanism exploration indicated that
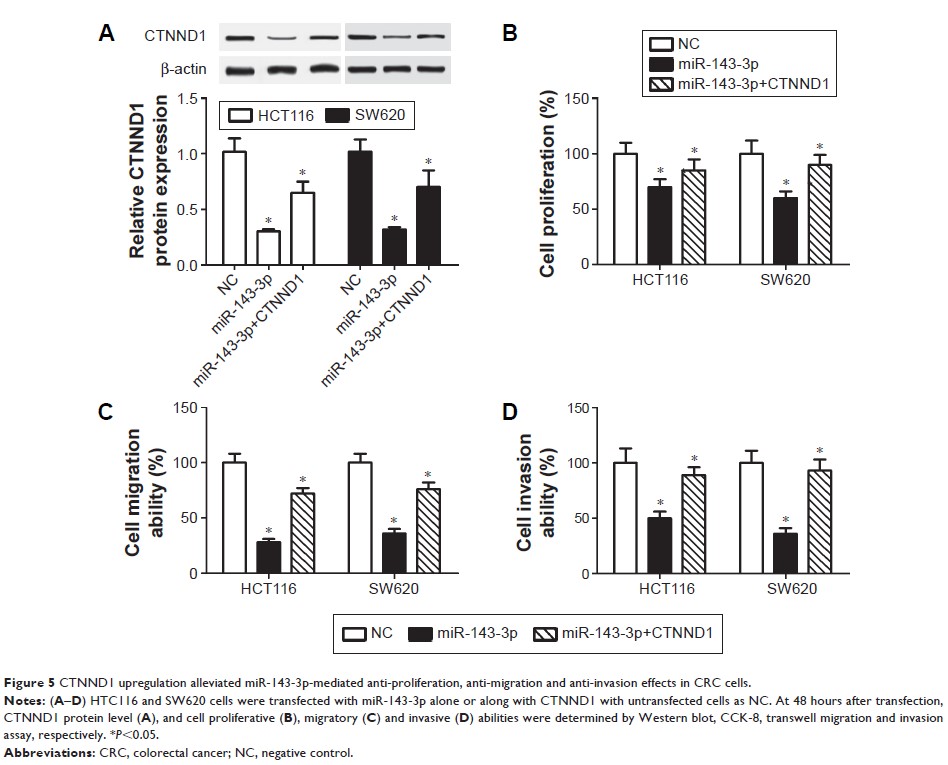
miR-143-3p directly targeted CTNND1. Moreover, enforced expression of CTNND1
contributed to cell proliferation, migration and invasion in CRC, and CTNND1
silencing exerted opposite effects. Restoration experiments disclosed that
CTNND1 upregulation weakened the inhibitory effects of miR-143-3p on CRC cell
proliferation, migration and invasion. Additionally, miR-143-3p inhibited the
growth of HCT116-derived xenograft tumors by targeting CTNND1 in vivo.
Conclusion: miR-143-3p
hampered the development and progression of CRC by targeting CTNND1
in vitro and in vivo, deepening our understanding of the functions
and molecular basis of miR-143-3p in the tumorigenesis of CRC and providing
some candidate prognostic markers or therapeutic targets for CRC.
Keywords: microRNA-143-3p,
CTNND1, colorectal cancer, tumorigenesis