110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

负载盐酸青藤碱的抗氧化剂的表面醇质化可增强透皮渗透性和类风湿性关节炎的药物沉积
Authors Song H, Wen J, Li H, Meng Y, Zhang Y, Zhang N, Zheng W
Received 26 September 2018
Accepted for publication 19 March 2019
Published 1 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3177—3188
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S188842
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Transdermal
drug delivery system (TDDS) curing rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for long-term
treatment can improve patients’ compliance and reduce the accumulation of drug
side effects. However, TDDS is constrained by the tight junction of the stratum
corneum and low permeation efficiency. It is necessary to adopt proper
permeation methods to ensure the therapeutic effect. The transethosome (TE),
which is derived from transfersome and ethosome (E), containing a high content
of ethanol along with an edge activator or permeation enhancer, has superior
deformability and higher permeation efficiency.
Methods and Results: In this
study, sinomenine hydrochloride-loaded TE was decorated with ascorbic acid to
form antioxidant surface transethosome (AS-TE). It was revealed that TE and
AS-TE containing sodium deoxycholate can effectively increase the entrapment
efficiency of hydrophilic drug, and has superior deformability and higher
permeation efficiency than E group. The plasma pharmacokinetics of rabbits
showed that TE group and AS-TE group had similar blood concentration and
bioavailability; however, micro-dialysis on synovial fluid demonstrated that
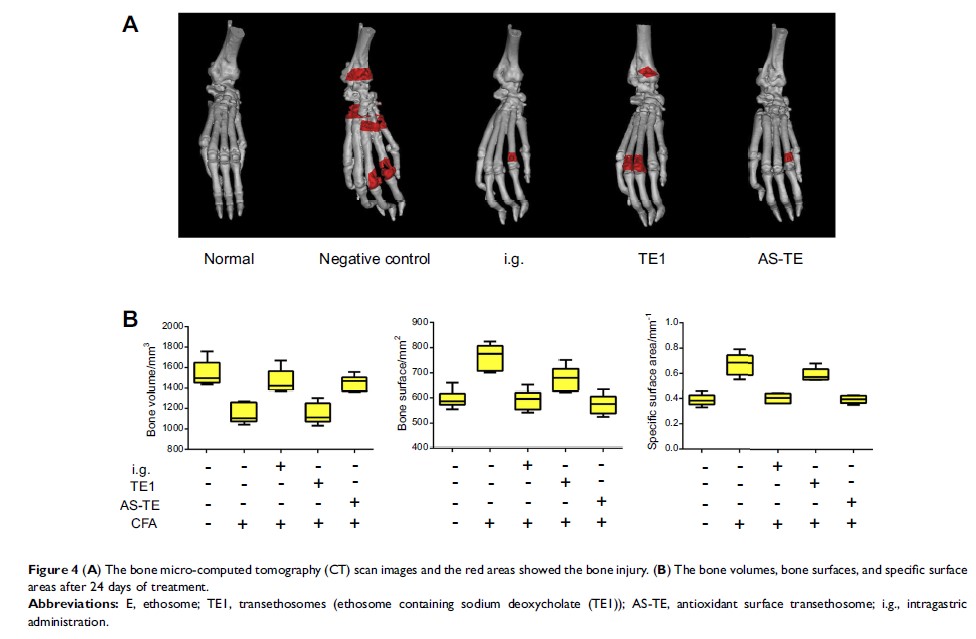
AS-TE group had higher drug concentration. In RA rat models, the alleviation of
the joint swell of AS-TE group was more obvious in the course of 3 weeks of
treatment. The inflammatory cytokines and erythrocyte sedimentation rate were
significantly lower than those in the negative control group and TE1 group.
Conclusion: AS-TE,
which can enhance transdermal permeability and drug deposition for the oxidant
stress of RA, had further research potential to serve as a TDDS of RA.
Keywords: transdermal
drug delivery system, antioxidant surface, transethosome, oxidant stress,
micro-dialysis