110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

基于磷脂复合物的纳米乳剂系统用于口服胰岛素递送:制备、体外和体内评估
Authors Hu XB, Tang TT, Li YJ, Wu JY, Wang JM, Liu XY, Xiang DX
Received 13 December 2018
Accepted for publication 11 March 2019
Published 1 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3055—3067
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S198108
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: The aim of this
research was to develop a phospholipid complex based nanoemulsion system for
oral insulin delivery.
Methods: Insulin-phospholipid
complex (IPC) was firstly prepared by an anhydrous co-solvent lyophilization
method, and then encapsulated into the oil phase of nanoemulsion to obtain the
IPC-based nanoemulsion (IPC-NE). Both water-in-oil (W/O) IPC-NE and
oil-in-water (O/W) IPC-NE were formulated and evaluated for comparison.
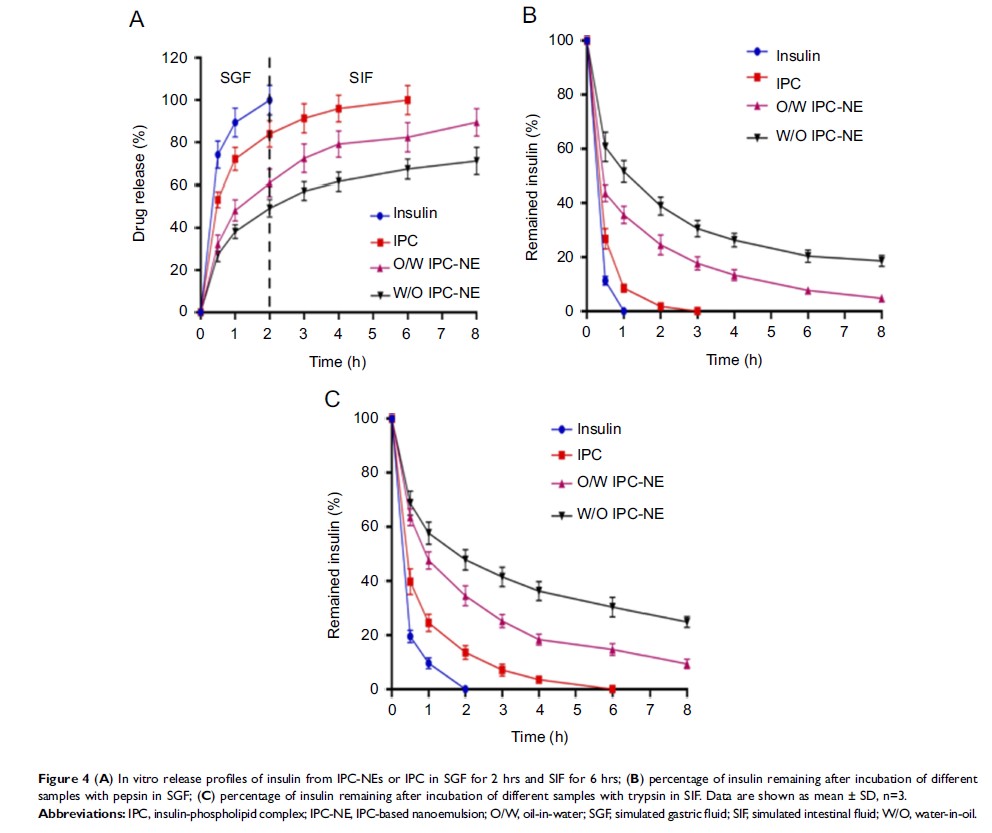
Results: The obtained
W/O IPC-NE and O/W IPC-NE were both spherical in shape with a mean particle
size of 18.6±0.79 nm and 27.3±1.25 nm, respectively. While both IPC-NEs
exhibited enhanced Caco-2 cell monolayers permeability than IPC and insulin
solution, W/O IPC-NE showed relatively greater protective effects against
enzymatic degradation than O/W IPC-NE. Moreover, oral administration of W/O
IPC-NE exhibited significant hypoglycemic effects, with 12.4-fold and 1.5-fold
higher oral bioavailability compared with insulin solution and O/W IPC-NE,
respectively.
Conclusion: IPC-NEs,
especially the W/O IPC-NE showed promising efficiency in vitro and in vivo,
thus could be a potential strategy for oral insulin delivery.
Keywords: insulin,
phospholipid complex, oral drug delivery, nanoemulsion, hypoglycemic effect