110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

胱抑素 SN 在肿瘤中的研究进展
Authors Liu Y, Yao J
Received 12 November 2018
Accepted for publication 15 February 2019
Published 6 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3411—3419
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S194332
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Federico Perche
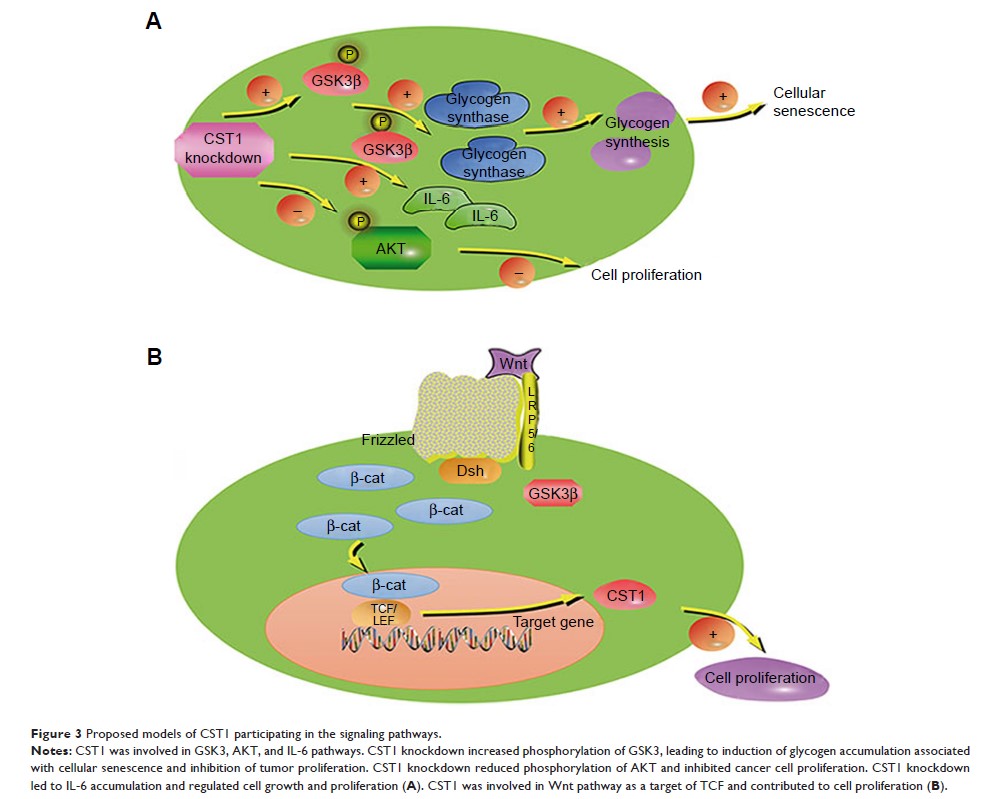
Abstract: Cystatin
SN, belonging to the type 2 cystatin superfamily, is widely expressed and
distributed in mammals. Cystatin SN is involved in inflammation, cell cycle,
cellular senescence, tumorigenesis, and metastasis. Cystatin SN is also known
to participate in signaling pathways like Wnt signaling pathway, GSK3 signaling
pathway, AKT signaling pathway, and IL-6 signaling pathway. Cystatin SN was
found to be highly expressed in peritumoral normal tissues in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC); however, low cystatin SN expression was found
in ESCC cancer tissues. Conversely, in other cancer types such as lung cancer,
breast cancer, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, and colorectal cancer, high
cystatin SN expression in cancer tissues but low cystatin SN expression in
peritumoral normal tissues was found. Survival analyses showed that high
cystatin SN expression benefited ESCC patients but did harm to other types of
cancer patients. Univariate and multivariate analyses indicated that cystatin
SN possibly acts as a marker for cancer prognosis. Here, we provide a brief
introduction about the role of cystatin SN in cancer and discuss the different
prognostic effects of cystatin SN on different tumors. Cystatin SN might be a
potential marker for cancer prognosis and a target for cancer therapy.
Keywords: cystatin,
cancers, signaling pathway, inflammation