110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长非编码 RNA CASC2 作为 microRNA-21 的 ceRNA 促进口腔鳞状细胞癌中 PDCD4 的表达
Authors Pan L, Chen H, Bai Y, Wang Q, Chen L
Received 20 December 2018
Accepted for publication 15 February 2019
Published 6 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3377—3385
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S198970
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Shreya Arora
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Prof. Dr. Geoffrey Pietersz
Background: Oral squamous
cell carcinoma (OSCC) is a common oral disease with high morbidity and
mortality. Recently, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were identified as critical
regulators in OSCC tumorigenesis. The present study aimed to work out the
functions and the possible molecular mechanisms of lncRNA CASC2 in human OSCC.
Methods: The
expression levels of CASC2 in clinical OSCC tissue samples and cultured OSCC
cell lines were detected by RT-qPCR analysis. MTT assay was performed to detect
the proliferation ability of OSCC cells, whereas the apoptosis rate and cell
cycle distribution of OSCC cells were determined by flow cytometric analysis.
The expression levels of relevant proteins were detected by Western blot assay.
Dual-luciferase reporter assay was performed to validate the predicted
relationship between CASC2, miR-21 amd PDCD4. The role of CASC2 in OSCC
tumorigenesis in vivo was evaluated using a nude mouse tumor model.
Results: The results
demonstrated that CASC2 was significantly downregulated in clinical OSCC tissue
samples and cultured OSCC cell lines. Low CASC2 expression was closely
correlated with adverse clinicopathological characteristics of OSCC patients.
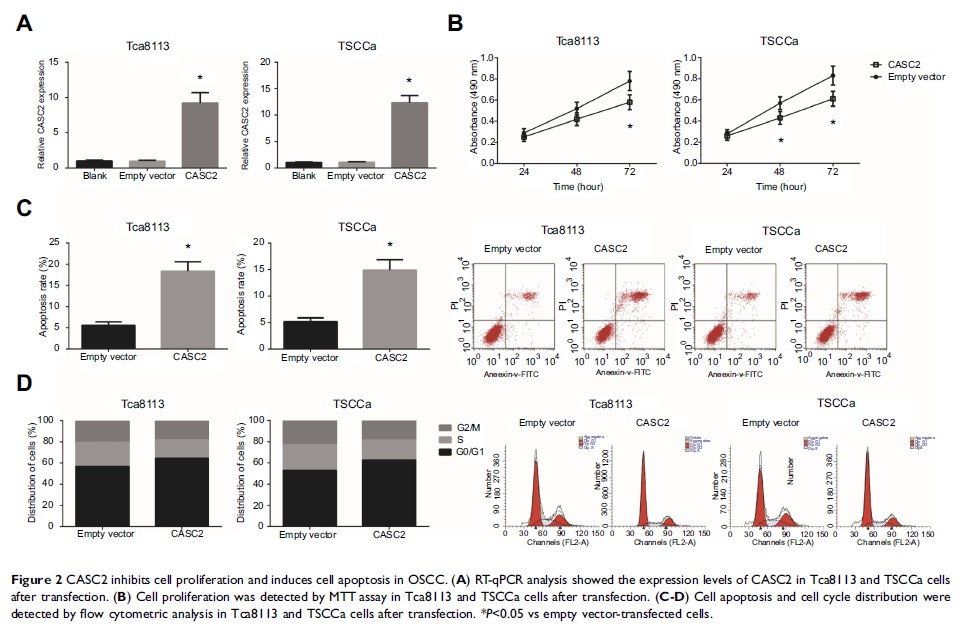
Functionally, overexpression of CASC2 remarkably inhibited cell proliferation
partly through inducing cell cycle arrest and cell apoptosis. Furthermore,
bioinformatics analysis and dual-luciferase reporter assay showed that CASC2
might act as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-21 to promote the expression of
PDCD4. Rescue experiments also showed that miR-21 blocked the tumor-suppressive
role that CASC2 exerted in OSCC cells. Finally, in vivo study indicated that
overexpression of CASC2 restrained OSCC tumor growth in volume and weight.
Conclusion: In conclusion,
these findings indicate that CASC2/miR-21/PDCD4 axis might be a potential
regulator of OSCC tumorigenesis, and shed new light on lncRNA-directed
diagnostics and therapeutics in OSCC.
Keywords: oral
squamous cell carcinoma, long non-coding RNA, CASC2, microRNA-21, PDCD4