110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

KIAA1429 通过改变 ID2 RNA 甲基化修饰(m6A)来调节肝细胞癌的迁移和侵袭
Authors Cheng X, Li M, Rao X, Zhang W, Li X, Wang L, Huang G
Received 20 July 2018
Accepted for publication 13 January 2019
Published 7 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3421—3428
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S180954
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Yao Dai
Purpose: N6-methyladenosine
(m6A), the most abundant mRNA modification in mammals, is involved in various
biological processes. KIAA1429 is an important methyltransferase participating
in m6A modification. However, the role of KIAA1429 in hepatocellular carcinoma
(HCC) is still not well understood. Here, we aimed to investigate the function
of KIAA1429 and its corresponding regulation mechanisms in HCC.
Patients and methods: HCC-related
genes were analyzed by clinical and expression data of HCC patients in The
Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Expression of KIAA1429 was verified by
quantitative reverse-transcription PCR, and interference efficiency was
obtained using small interfering RNA (siRNA). Cell proliferation, migration,
and invasion were assessed by cell counting kit-8 and transwell assays,
and the m6A modification was detected by methylated RNA immunoprecipitation-PCR
(MeRIP-PCR).
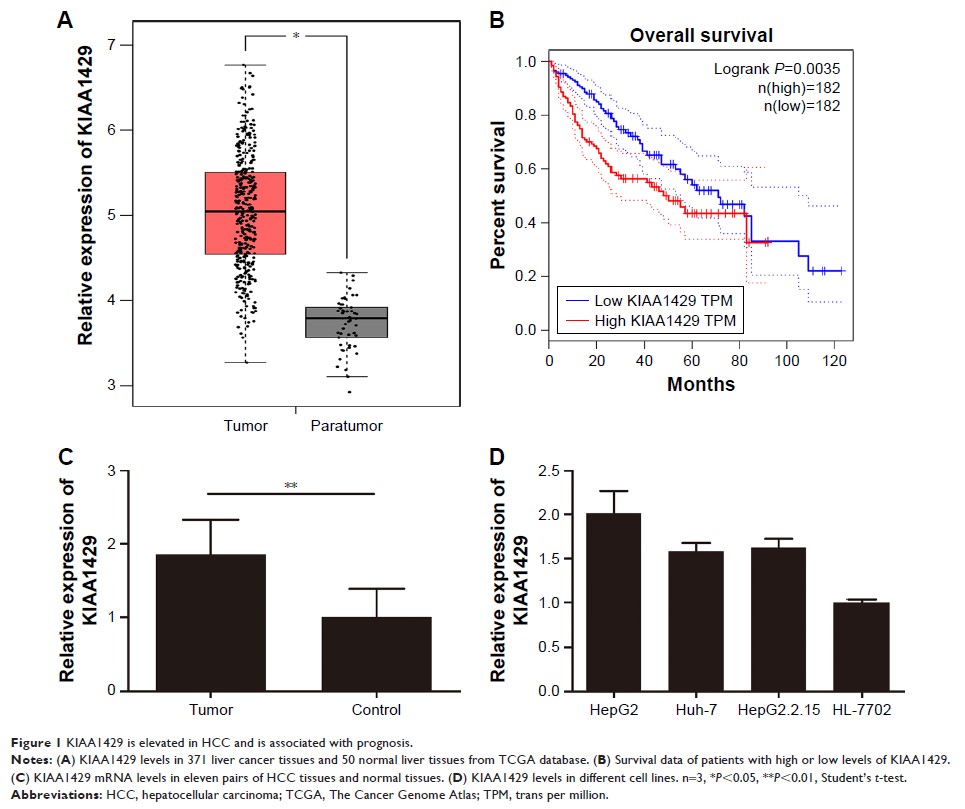
Results: We found
a difference in the expression of KIAA1429 between HCC and normal hepatic
tissues by analyzing data from the TCGA database. Comparing HCC cell lines
(HepG2, Huh-7, HepG2.2.15) with normal hepatic cells (HL-7702), we observed an
identically significant difference in KIAA1429 expression. KIAA1429
significantly enhanced proliferation, migration, and invasion of HepG2 cells.
Moreover, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes functional enrichment
analysis and correlation analysis revealed a significant negative correlation
between KIAA1429 and ID2. In the subsequent MeRIP-PCR assay, downregulation of
KIAA1429 inhibited m6A modification of ID2 mRNA.
Conclusion: KIAA1429
facilitated migration and invasion of HCC by inhibiting ID2 via upregulating
m6A modification of ID2 mRNA.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine,
methyltransferases, tumor metastasis, invasion