110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长期淫羊藿苷治疗通过由 CD4+ T 细胞介导的免疫炎症反应改善 APP/PS1 小鼠的认知缺陷
Authors Zhu T, Zhang F, Li H, He Y, Zhang G, Huang N, Guo M, Li X
Received 8 March 2019
Accepted for publication 15 April 2019
Published 7 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 817—826
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S208068
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
Background: Alzheimer’s
disease (AD) is the most common neurodegenerative disorder that also involves
neuroinflammation in addition to many other features. Icariin (ICA) as one of
the active ingredients of Chinese herbal medicine has the immunomodulating
function. This study aimed to investigate the immunotherapeutic potential of
ICA on AD.
Methods: APP/PS1
mice and wild type C57BL/6 mice were subjected to orally ICA administration (60
mg/kg/d) for 8 months. Then, the ethological and biochemical experiments, such
as Morris water maze assay, Aβ ELISA, blood T cell flow cytometry, and plasma
and brain cytokines array, were conducted to evaluate the effects of ICA
administration.
Results: ICA
significantly improved spatial learning and memory retention in APP/PS1 mice.
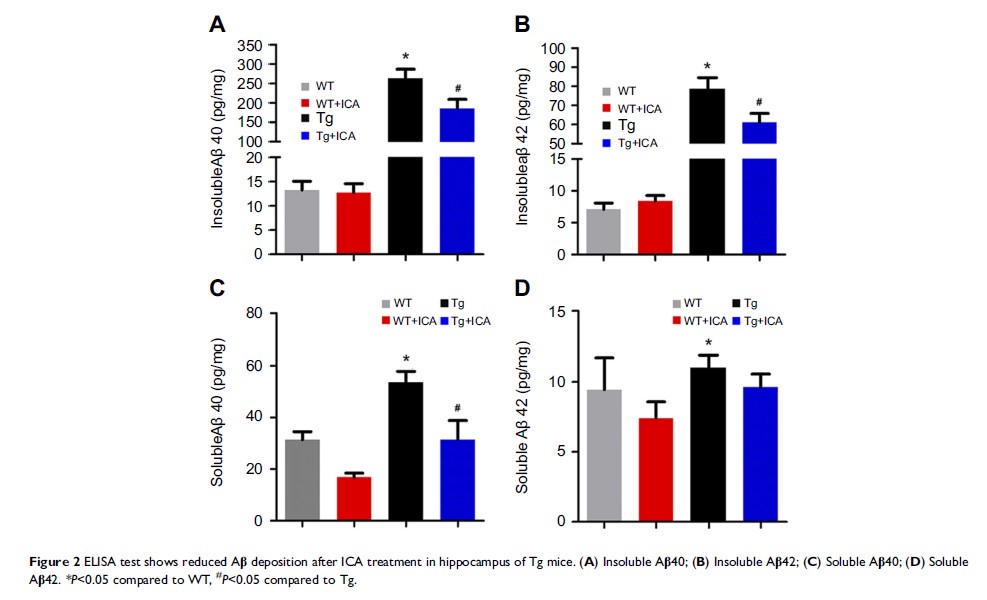
Long-term application of ICA could also reduce hippocampus Aβ deposition,
modulate the differentiation of CD4+ T cells, and modulate the release of
inflammatory cytokines in plasma and brain tissue.
Conclusion: ICA shows
the neuroprotective effects via modulating the CD4+ T
lymphocyte-related immuno-inflammatory responses in APP/PS1 mice and may be a
promising drug against AD progression.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s
disease, icariin, T lymphocyte, neuroinflammation, cytokines