110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

FLT3-ITD 和 NPM1 双突变的急性髓细胞白血病患者应接受 CR1 的异基因造血干细胞移植,以获得更好的预后
Authors Huang Y, Hu J, Lu T, Luo Y, Shi J, Wu W, Han X, Zheng W, He J, Cai Z, Wei G, Huang H, Sun J
Received 25 November 2018
Accepted for publication 22 March 2019
Published 8 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4129—4142
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S194523
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: According to the recent National
Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines, the risk level in acute myeloid
leukemia (AML) patients with FLT3-ITD and NPM1 double
mutation (AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ ) depends on
the allelic ratio of FLT3-ITD . But despite a low or high allelic ratio
of FLT3-ITD ,
AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ patients
belong to the favorable or intermediate risk, for whom allogeneic stem cell
transplantation is not obligated. However, some latest studies pointing out
that NPM1 and FLT3-ITD double
mutation patients showed an inferior prognosis, which have raised concern about
the risk categorization and more effective treatment of AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ patients.
Methods: A
total of 76 patients were selected for coexisting FLT3 and NPM1 mutations
with normal cytogenetics. The prognostic risk factors were analyzed, and
treatment strategies including allogeneic stem cell transplantati1on and
chemotherapy were compared.
Results: In
76 AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ patients,
36.8% of patients had hyperleukocytosis (HL) and DNMT3A R882 mutation
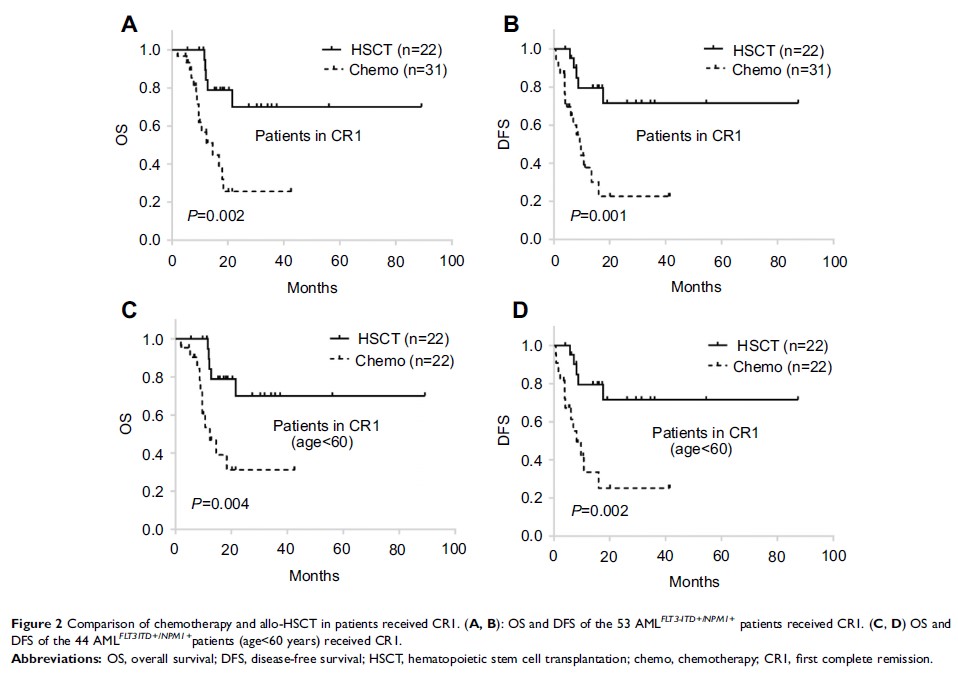
was the most common concomitant gene (23.7%). For 53 patients in the complete
remission (CR), 22 had received allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell
transplantation (allo-HSCT) on first complete remission (CR1). Patients in
transplantation group had better overall survival (OS) and disease-free
survival (DFS) than chemotherapy only (P =0.002 and 0.001, respectively). In multivariable Cox
model analyses, HL and DNMT3A R882 mutation were independent adverse
prognostic factors (all P <0.05) for AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ patients. Nevertheless, allo-HSCT was an
independent good factor of OS and DFS (P =0.001 and 0.000; HR =0.173 and 0.138; 95% CI were
0.062–0.483 and 0.049–0.389). And allo-HSCT could moderately improve the poor
prognosis of AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+/DNMT3A R882+ .
Conclusion: Although,
AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ patients are categorized as favorable or
intermediate risk levels according to recent NCCN and ELN guidelines, these
patients should receive allo-HSCT in CR1 for a longer survival. AMLFLT3-ITD+/NPM1+ patients with DNMT3A R882 mutation
had a very poor prognosis, and allo-HSCT could moderately improve their
survival.
Keywords: FLT3-ITD , NPM1 , DNMT3A R882 ,
allo-HSCT