110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

PD-L1 在尿路上皮癌中的临床病理和预后价值:一项荟萃分析
Authors Ding X, Chen Q, Yang Z, Li J, Zhan H, Lu N, Chen M, Yang Y, Wang J, Yang D
Received 12 June 2018
Accepted for publication 7 March 2019
Published 8 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4171—4184
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S176937
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Rituraj Purohit
Objective: Our
objective was to conduct a meta-analysis to investigate the clinicopathological
features and prognostic value of programmed cell death ligand 1 (PD-L1)
expression in patients with urothelial carcinoma (UC).
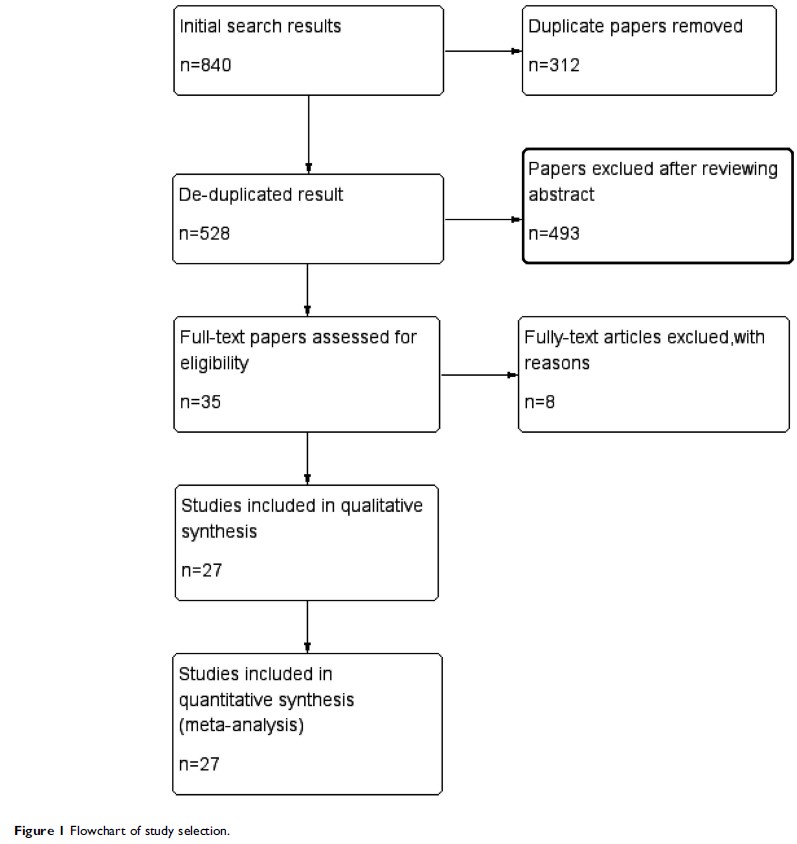
Materials and Methods: Twenty-seven
studies with 4,032 patients were included in the meta-analysis. Pooled ORs and
95% CIs were used to examine the associations between clinical factors and
PD-L1 expression. HRs and 95% CIs were extracted from eligible studies.
Heterogeneity was evaluated using the chi-squared-based Q test and I2, statistic.
Results: Expression
of PD-L1 on tumor cells (TCs) was associated with muscle-invasive disease
(OR=3.67, 95% CI: 2.53–5.33), and inversely associated with the history of
intravesical bacilli Calmette-Guerin therapy (OR=0.39, 95% CI: 0.18–0.82) in
bladder cancer patients. PD-L1 expression on TCs was associated with worse
overall survival (HR=2.06, 95% CI: 1.38–3.06) in patients with organ-confined
bladder cancer. PD-L1 expression in patients with UC was significantly related
to better objective response rate after PD-1/PD-L1 antibody treatment.
Conclusions: Expression
of PD-L1 on TCs was associated with muscle-invasive disease in patients with
bladder cancer. Patients with PD-L1-positive UC had a significantly better
response to PD-1/PD-L1 targeted treatment.
Keywords: urothelial
carcinoma, programmed cell death ligand 1, immunotherapy, meta-analysis,
prognosis