110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

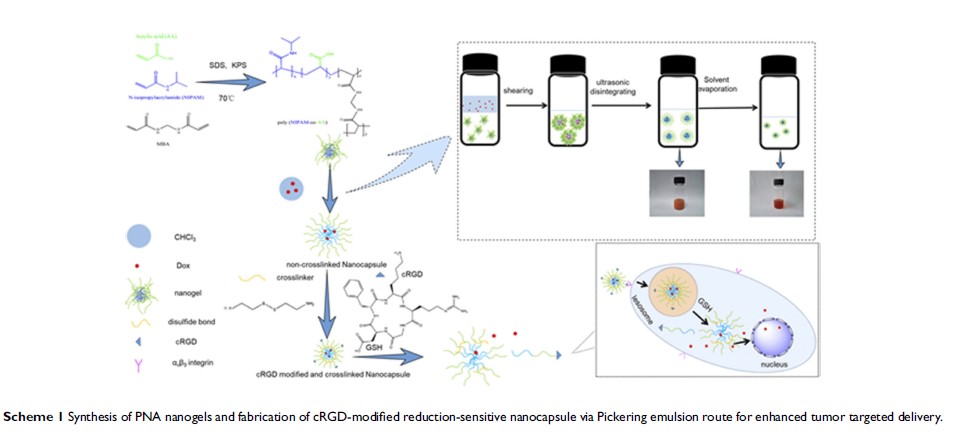
通过 Pickering 乳液途径制备经 cRGD 修饰的还原敏感性纳米胶囊以促进肿瘤靶向递送
Authors Shang X, Liu Q, Qin T, Xu X, Sun H, Liu M, Zhu H
Received 21 January 2019
Accepted for publication 4 March 2019
Published 8 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3361—3373
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S202063
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Mian Wang
Purpose: To
fabricate multifunctional nanocapsule via Pickering emulsion route to
facilitate tumor-targeted delivery.
Methods: Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic
acid) nanoparticles (PNA) stabilized nanocapsules were fabricated by Pickering
emulsion (PE) technology. For controllable drug-release and enhancing targeted
antitumor effects, the nanocapsules were crosslinked with cystamine and coupled
on cell-surface molecule markers (cRGDfK) to achieve on-demand drug release and
targeted delivery.
Results: The
fabricated PE and nanocapsules with average particle sizes (250 and 150 nm)
were obtained. Encapsulation efficiency of hydrophobic anticancer drug (DOX)
was determined as >90%. Release kinetic profiles for encapsulated
nanocapsules displayed circulation stability and redox-sensitive releasing
behavior with the supposed increase bioavailability. Both cytotoxicity assay,
cellular uptake analysis and anticancer efficacy in B16F10 murine model
demonstrated these redox-responsive drug-release and active targeted delivery.
Conclusion: The
results clearly demonstrated nanocapsule via PE route as promising candidate to
provide an effective platform for incorporating hydrophobic drug for targeted
cancer chemotherapy.
Keywords: nanocapsule,
Pickering emulsion, control release, tumor-targeted delivery