110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

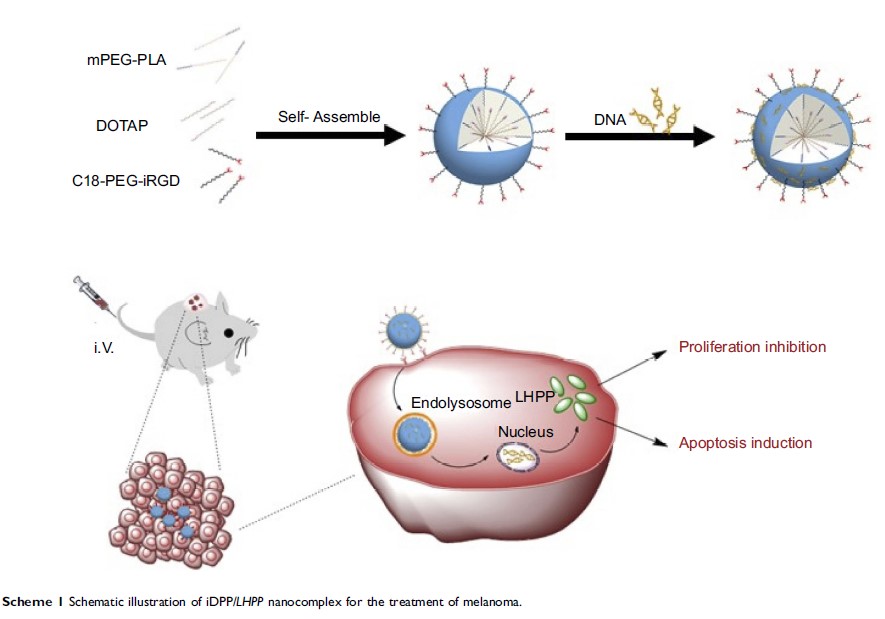
靶向纳米颗粒介导的 LHPP 用于黑素瘤治疗
Authors Zhang Q, Xiong M, Liu J, Wang S, Du T, Kang T, Liu Y, Cheng H, Huang M, Gou M
Received 29 November 2018
Accepted for publication 12 March 2019
Published 10 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3455—3468
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S196374
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Govarthanan Muthusamy
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Linlin Sun
Background: Phospholysine
phosphohistidine inorganic pyrophosphate phosphatase (LHPP) is a novel tumor
suppressor. However, whether LHPP is effective to melanoma has not been
investigated. Gene therapy provides a new strategy for the treatment of
melanoma. Currently, it suffers from the lack of safe and effective gene
delivery systems.
Methods: A
CRGDKGPDC peptide (iRGD) modified hybrid monomethoxy poly(ethylene
glycol)-poly(D,L-lactide) nanoparticle (iDPP) was prepared and
complexed with a LHPP plasmid, forming an iDPP/LHPP nanocomplex.
The iDPP/LHPP nanocomplex
was characterized by particle size distribution, zeta potential, morphology,
cytotoxicity, and transfection efficiency. The antitumor efficacy of the
nanocomplex against melanoma was studied both in vitro and in vivo. Further,
the potential epigenetic changes in melanoma induced by iDPP/LHPP nanocomplex
were evaluated.
Results: The iDPP/LHPP nanocomplex
showed high transfection efficiency and low toxicity. Moreover, the nanocomplex
displayed a neutral charge that can meet the requirement of intravenous
injection for targeted gene therapy. In vitro and in vivo experiments indicated
that the iDPP/LHPP nanocomplex
significantly inhibited the melanoma growth without causing notable adverse
effects. We also found that LHPP played an important role in epigenetics. It
regulated the expression of genes related to the proliferation and apoptosis
chiefly at the level of transcription.
Conclusion: This work
demonstrates that the iDPP nanoparticle-delivered LHPP gene has
a potential application in melanoma therapy through regulation of the genes
associated with epigenetics.
Keywords: melanoma,
LHPP, nanoparticle, gene therapy, epigenetics