110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

血脑屏障通透性与血管周围区域空间扩大的关系:一项横断面研究
Authors Li Y, Li M, Yang L, Qin W, Yang S, Yuan J, Jiang T, Hu W
Received 5 February 2019
Accepted for publication 15 April 2019
Published 10 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 871—878
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S204269
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Justinn Cochran
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Zhi-Ying Wu
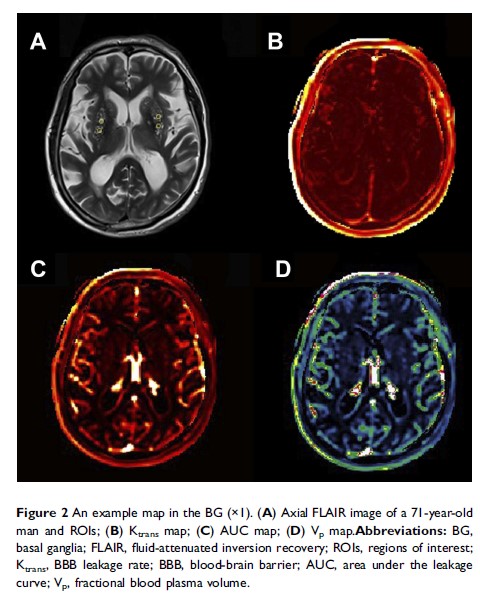
Purpose: Enlarged
perivascular spaces (EPVS) have been widely considered as a feature of cerebral
small vessel disease (cSVD) but the pathogenesis of EPVS remains unclear.
Compromised blood–brain barrier (BBB) integrity may play a role since previous
studies have shown that BBB breakdown is a critical contributor to the
pathogenesis of other cSVD markers. This study aimed to investigate the
association of EPVS in the centrum semiovale (CSO) and basal ganglia (BG) with
BBB permeability.
Patients and methods: Consecutive
participants free of symptomatic stroke history presented for physical
examination were enrolled in this cross-sectional study. CSO- and BG-EPVS on
T2-weighted (T2-W) magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were rated using a
five-point validated scale. Dynamic contrast-enhanced (DCE)-MRI and Patlak
pharmacokinetic model were applied to quantify BBB permeability in the CSO and
BG.
Results: A total
of 109 participants aged 49–90 years (mean age of 69.85 years) were enrolled.
The proportions of participants presenting high-grade (>10) EPVS in the CSO
and BG were 50.5% and 44.0%, respectively. After adjustments for potential
confounders by logistic regression, leakage rate and fractional blood plasma
volume were correlated with the severity of BG-EPVS (OR: 5.33; 95%CI:
1.95–14.60 and OR: 0.93; 95%CI: 0.87–0.99).
Conclusion: Our study
demonstrates that BG-EPVS are associated with compromised BBB integrity,
supporting the hypothesis that the BBB dysfunction may be involved in the
pathogenesis of BG-EPVS. EPVS in the CSO and BG may have distinct
pathophysiology.
Keywords: enlarged
perivascular spaces, cerebral small vessel disease, blood–brain barrier,
dynamic contrast-enhanced, DCE, magnetic resonance imaging, MRI