110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

生物钟基因在肿瘤中的作用
Authors Li HX
Received 28 January 2019
Accepted for publication 10 April 2019
Published 13 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3645—3660
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S203144
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 4
Editor who approved publication: Dr Leo Jen-Liang Su
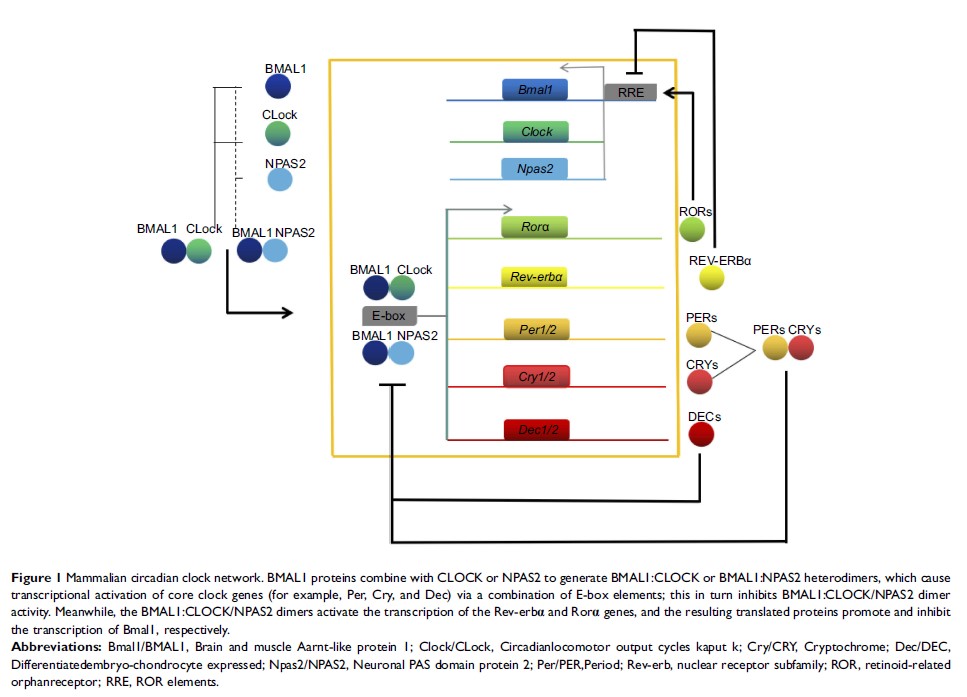
Abstract: Circadian
rhythms are generated via variations in the expression of clock genes that are
organized into a complex transcriptional–translational autoregulatory network
and regulate the diverse physiological and behavioral activities that are
required to adapt to periodic environmental changes. Aberrant clock gene
expression is associated with a heightened risk of diseases that affect all
aspects of human health, including cancers. Within the past several years, a
number of studies have indicated that clock genes contribute to carcinogenesis
by altering the expression of clock-controlled and tumor-related genes
downstream of many cellular pathways. This review comprehensively summarizes
how clock genes affect the development of tumors and their prognosis. In
addition, the review provides a full description of the current state of oral
cancer research that aims to optimize cancer diagnosis and treatment
modalities.
Keywords: circadian
rhythms, clock genes, oral squamous cell carcinoma, carcinogenesis, oral cancer