110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

长链非编码 RNA FEZF1-AS1 通过 Wnt/β-catenin 途径促进食管鳞状细胞癌的运动性
Authors Yang L, Ye Y, Chu J, Jia J, Qu Y, Sun T, Yin H, Ming L, Wan J, He F
Received 26 November 2018
Accepted for publication 17 March 2019
Published 13 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4425—4435
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S196004
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
Background: Long
noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs), a class of noncoding RNA nucleotides >200 bp, has
been demonstrated to play vital role in the development of cancer. FEZ family
zinc finger 1 antisense RNA 1 (FEZF1-AS1) has been reported as an lncRNA which
acts as a tumor-promoting effect in some cancers. However, the role of it in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) and its potential regulatory
mechanism was unclear now.
Methods: qRT-PCR
was used to detect the levels of FEZF1-AS1 and mRNA CTNNB1 (β-catenin) in ESCC
tissues and cells. Cell transfection experiments were used to knock down or
overexpress the level of FEZF1-AS1 in EC1 and EC9706 cell lines. WST-1 assays,
cell cycle assays, scratch wound assays, migration, and invasion assays were
used to evaluate the function of FEZF1-AS1 in ESCC progression.
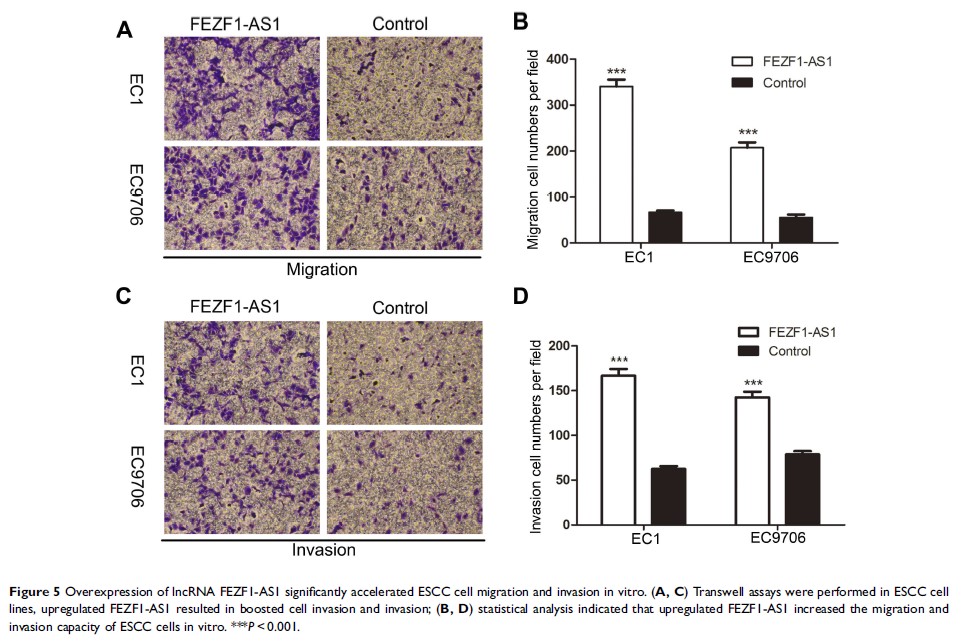
Results: FEZF1-AS1
was remarkably upregulated in ESCC tissues and cell lines. Silencing of
FEZF1-AS1 significantly inhibited the migration and invasion of ESCC cells,
while overexpression of FEZF1-AS1 notably accelerated ESCC migration and
invasion. Meanwhile, the levels of FEZF1-AS1 had no effect on ESCC cell
proliferation and cell cycle. We also found that β-catenin was upregulated in
ESCC tissues, and the level of it was positively correlated with the expression
of FEZF1-AS1. Silencing of FEZF1-AS1 could decrease the mRNA and protein level
of β-catenin, while overexpression FEZF1-AS1 could lead to the contrary.
Conclusion: Our
results suggested that the expression of lncRNA FEZF1-AS1 played an important
role in ESCC progression, especially the motility of the tumor. FEZF1-AS1 may
provide us with a new sight for ESCC treatment.
Keywords: esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma, lncRNA, FEZF1-AS1, biological function, β-catenin