110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

西莫替尼(一种新型特异性 EGFR 酪氨酸激酶抑制剂)应用于晚期非小细胞肺癌患者的安全性、耐受性和药代动力学:Ib 期试验结果
Authors Hu XS, Han XH, Yang S, Li N, Wang L, Song YY, Mu H, Shi YK
Received 8 October 2018
Accepted for publication 22 March 2019
Published 13 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4449—4459
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S189626
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Purpose: The aim
of this phase Ib study (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT01772732) was to assess safety,
tolerability, and pharmacokinetics (PKs) of simotinib (a novel EGFR tyrosine
kinase inhibitor) in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
and EGFR gene
mutation.
Patients and methods: 41
patients with EGFR gene mutations were enrolled and received
simotinib orally administered twice daily with dose escalating from 100 to 650
mg in 28 days cycle. Safety and tolerability were assessed through the study.
Blood samples were collected for PK analysis on Days 1, 8, 9, 10, 15, 22 and 29.
Tumor response was assessed at baseline, on Day 29 and every 8 weeks
thereafter.
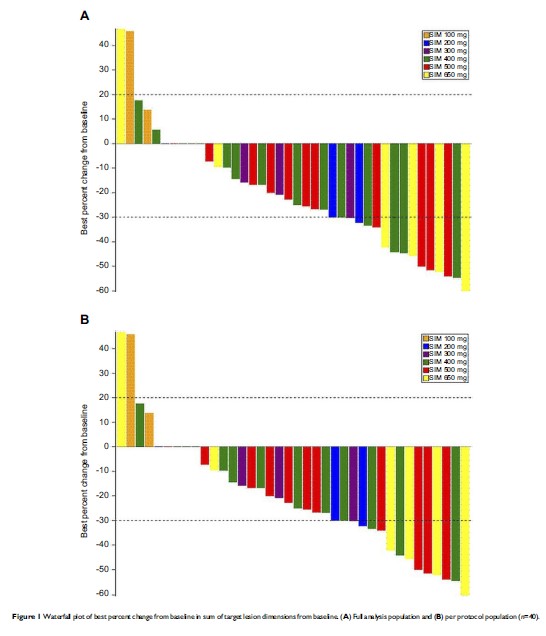
Results: Simotinib
was well tolerated, with no dose-limiting toxicities. Maximum tolerated dose
(MTD) was not found. 95.1% of patients experienced at least one adverse event
(AE), and most of them were mild or moderate. Rash (41.5%) and diarrhea (56.1%)
were the most frequently reported AEs. Simotinib was rapidly absorbed and
eliminated with average T max ranging
from 1 to 4 hrs and T 1/2 ranging
between 6.2 and 13.0 hrs after multiple-dose administration. No dose–response
relationship between dose and exposure was observed after multiple-dose
administration. 39.3% of the enrolled patients achieved a partial response and
46.3% had stable disease. Median progression-free survival and overall survival
were 9.9 (CI% 4.7; 12.1) months and 14.6 (95%CI 12.3; 22.5) months,
respectively.
Conclusion: Simotinib
was well tolerated, with manageable AEs at doses of up to 650 mg and MTD was
not reached. Further studies to explore higher doses are ongoing.
Keywords: simotinib,
EGFR, non-small cell lung cancer, toxicity, pharmacokinetics