110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

通过整合微阵列分析鉴定非小细胞肺癌中的新型生物标志物和候选小分子药物
Authors Wu Q, Zhang B, Sun Y, Xu R, Hu X, Ren S, Ma Q, Chen C, Shu J, Qi F, He T, Wang W, Wang Z
Received 18 December 2018
Accepted for publication 21 March 2019
Published 13 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3545—3563
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S198621
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Rachel Predeepa
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: Non-small-cell
lung cancer (NSCLC) remains the leading cause of cancer morbidity and mortality
worldwide. In the present study, we identified novel biomarkers associated with
the pathogenesis of NSCLC aiming to provide new diagnostic and therapeutic
approaches for NSCLC.
Methods: The
microarray datasets of GSE18842, GSE30219, GSE31210, GSE32863 and GSE40791 from
Gene Expression Omnibus database were downloaded. The differential expressed
genes (DEGs) between NSCLC and normal samples were identified by limma package.
The construction of protein–protein interaction (PPI) network, module analysis
and enrichment analysis were performed using bioinformatics tools. The
expression and prognostic values of hub genes were validated by GEPIA database
and real-time quantitative PCR. Based on these DEGs, the candidate small
molecules for NSCLC were identified by the CMap database.
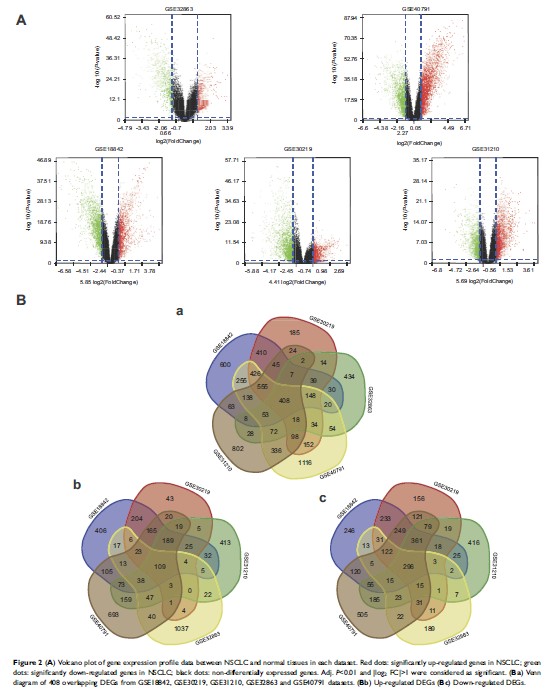
Results: A total
of 408 overlapping DEGs including 109 up-regulated and 296 down-regulated genes
were identified; 300 nodes and 1283 interactions were obtained from the PPI
network. The most significant biological process and pathway enrichment of DEGs
were response to wounding and cell adhesion molecules, respectively. Six DEGs
(PTTG1, TYMS, ECT2, COL1A1, SPP1 and CDCA5) which significantly up-regulated in
NSCLC tissues, were selected as hub genes according to the results of module
analysis. The GEPIA database further confirmed that patients with higher
expression levels of these hub genes experienced a shorter overall survival. Additionally,
CMap predicted the 20 most significant small molecules as potential therapeutic
drugs for NSCLC. DL-thiorphan was the most promising small molecule to reverse
the NSCLC gene expression.
Conclusions: Based on
the gene expression profiles of 696 NSCLC samples and 237 normal samples, we
first revealed that PTTG1, TYMS, ECT2, COL1A1, SPP1 and CDCA5 could act as the
promising novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets for NSCLC. Our work will
contribute to clarifying the molecular mechanisms of NSCLC initiation and
progression.
Keywords: non-small-cell
lung cancer, novel biomarkers, candidate small molecules, prognosis,
bioinformatics analysis