110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

β-TCP 纳米粒子抑制肝细胞癌的体外和体内机制
Authors Liu L, Dai H, Wu Y, Li B, Yi J, Xu C, Wu X
Received 2 November 2018
Accepted for publication 19 March 2019
Published 13 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3491—3502
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S193192
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Background: Studies
have showed that nanoparticles have a certain anti-cancer activity and can
inhibit many kinds of cancer cells. β-tricalcium phosphate nanoparticles
(nano-β-TCP) displays better biodegradation, but the application and mechanism
of nano-β-TCP in anti-cancer activity are still not clear.
Purpose: The
objective of this study was to synthesize nano-β-TCP and investigate its
inhibitory properties and mechanism on hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cells
in vitro and in vivo.
Methods: Nano-β-TCP
was synthesized using ethanol-water system and characterized. The effects of
nano-β-TCP on cell viability, cell uptake, intracellular oxidative stress
(ROS), cell cycle and apoptosis were also investigated with HepG2 cells and
human hepatocyte cells (L-02). Intratumoral injection of nano-β-TCP was performed
on the xenograft liver cancer model to explore the inhibitory effect and
mechanism of nano-β-TCP on liver tumors.
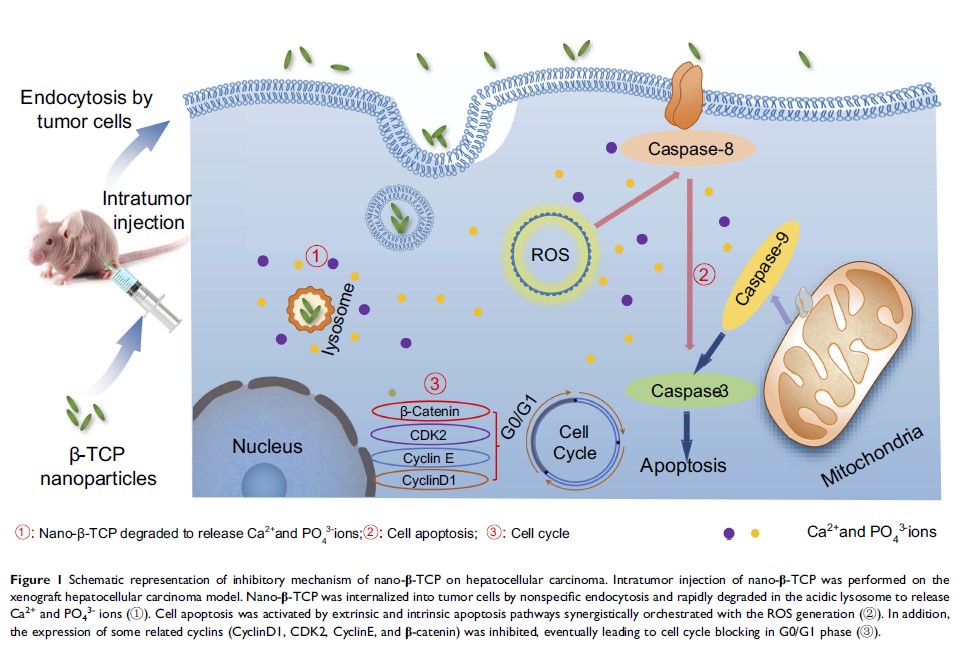
Results: In vitro
results revealed that nano-β-TCP caused reduced cell viability of HepG2 cells
in a time-and dose-dependent manner. Nano-β-TCP was internalized through
endocytosis and degraded in cells, resulting in obvious increase of the
intracellular Ca2+ and PO43- ions.
Nano-β-TCP induced cancer cells to produce ROS and induced apoptosis of tumor
cells by an apoptotic signaling pathways both in extrinsic and intrinsic
pathway. In addition, nano-β-TCP blocked cell cycle of HepG2 cells in G0/G1
phase and disturbed expression of some related cyclins. In vivo results showed
that 40 mg/kg of nano-β-TCP had no significant toxic side effects, but could
effectively suppress hepatocellular carcinoma growth.
Conclusion: These
findings revealed the anticancer effect of nano-β-TCP and also clarified the
mechanism of its inhibitory effect on hepatocellular carcinoma.
Keywords: nano-β-TCP,
HepG2 cells, ROS, cell cycle, apoptosis, inhibition