110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

鉴定和验证膀胱癌患者的个体化自噬临床预后指数
Authors Wang SS, Chen G, Li SH, Pang JS, Cai KT, Yan HB, Huang ZG, He RQ
Received 10 December 2018
Accepted for publication 22 March 2019
Published 14 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3695—3712
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197676
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Ms Aruna Narula
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Jianmin Xu
Purpose: Autophagy
is a major catabolic system by which eukaryotic cells undergo self-degradation
of damaged, defective, or unwanted intracellular components. An abnormal
autophagic level is implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple diseases,
including cancers. The aim of this study is to explore the prognostic value of
autophagy in bladder cancer (BC), which is a major cause of cancer-related
death globally.
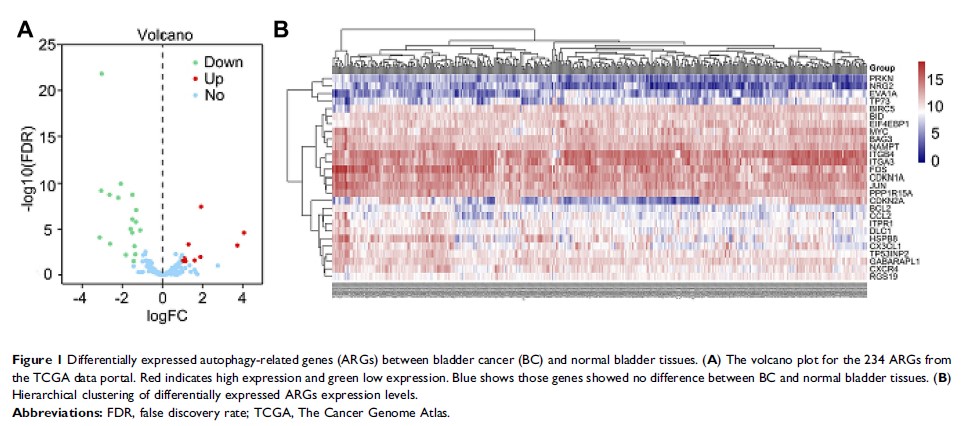
Patients and methods: First, 27
differentially expressed autophagy-related genes (ARGs) were identified in BC
patients based on The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database. Functional
enrichment analyses hinted that autophagy may act in a tumor-suppressive role
in the initiation of BC. Then, the Cox proportional hazard regression model
were employed to identify three key prognostic ARGs (JUN, MYC, and ITGA3),
which were related with overall survival (OS) significantly in BC. The three
genes represented important clinical significance and prognostic value in BC.
Then a prognostic index (PI) was constructed.
Results: The PI
was constructed based on the three genes, and significantly stratified BC
patients into high- and low-risk groups in terms of OS (HR=1.610, 95%
CI=1.200–2.160, P =0.002). PI remained as an independent prognostic
factor in multivariate analyses (HR=2.355, 95% CI=1.483–3.739, P <0.001). When
integrated with clinical characteristics of age and stage, an
autophagy-clinical prognostic index (ACPI) was finally validated, which had
improved performance in predicting OS of BC patients (HR=2.669, 95%
CI=1.986–3.587, P <0.001). The ACPI was confirmed in datasets of
GSE13507 (HR=7.389, 95% CI=3.645–14.980, P <0.001) and
GSE31684 (HR=1.665, 95% CI=0.872–3.179, P =0.122).
Conclusion: This
study provides a potential prognostic signature for predicting prognosis of BC
patients and molecular insights of autophagy in BC.
Keywords: autophagy-related
genes, prognostic index, bladder cancer, The Cancer Genome Atlas