110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

芦荟大黄素对宫颈癌细胞的抗肿瘤作用与人乳头瘤病毒 E6/E7 及糖代谢有关
Authors Gao R, Wu X, Huang Z, Wang B, Li F, Xu H, Ran L
Received 2 August 2018
Accepted for publication 21 February 2019
Published 14 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3713—3721
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S182405
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Sanjay Singh
Background: Aloe-emodin,
an anthraquinone present in aloe latex, has been shown to have
anti-proliferative properties in cervical cancer disease, all cases of which
are almost caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), with the products of E6/E7. It
is suggested that aloe-emodin may play an important role in HPV-induced
cervical cancer cells.
Methods: Hela and
SiHa cells were treated with various concentrations of aloe-emodin. MTT assay
and flow cytometry were used to identify the cell growth and apoptosis. The expressions
of HPV E6, E7 and GLUT1 (glucose transporter-1) were detected by real-time
quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot (WB). The
glucose uptake, lactate production and ATP production in HeLa and SiHa cells
were also investigated.
Result: The
results indicate that aloe-emodin promoted the apoptosis of HeLa and SiHa cells
and decreased the expressions of HPV-related protein E6 and E7. Furthermore,
aloe-emodin inhibited glucose metabolism by reducing GLUT1 expression.
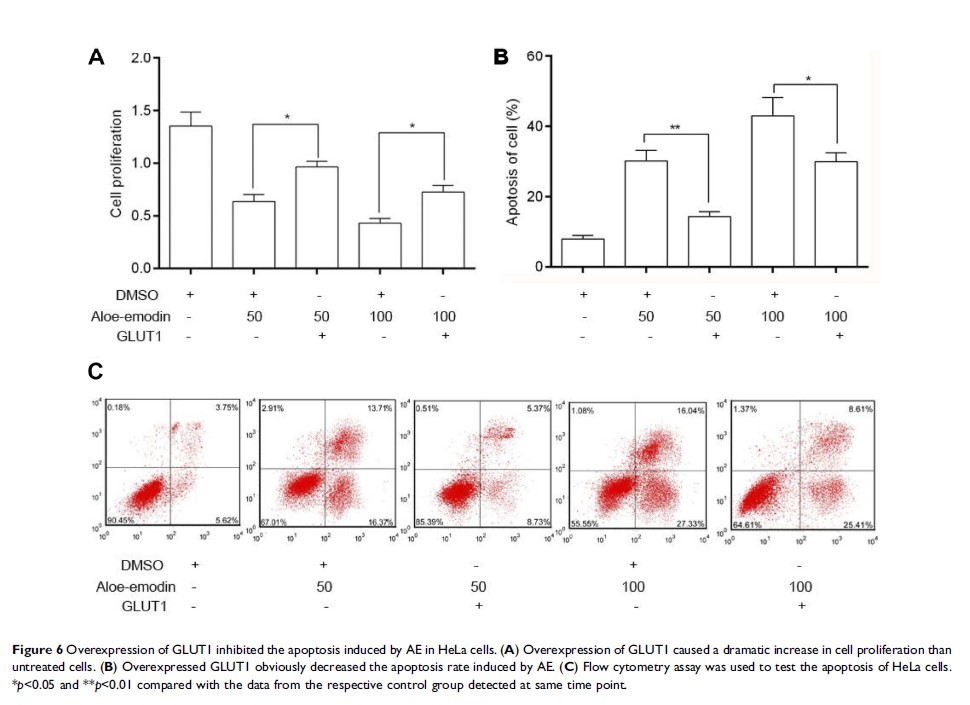
Overexpression of GLUT1 significantly weakened the apoptosis induced by
aloe-emodin in HeLa cells.
Conclusion: In this
study, we found that aloe-emodin induce apoptosis of cervical cancer cells,
which was associated with HPV E6 and E7 and glucose metabolism.
Keywords: cervical
cancer, aloe-emodin, E6/E7, glucose metabolism