110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

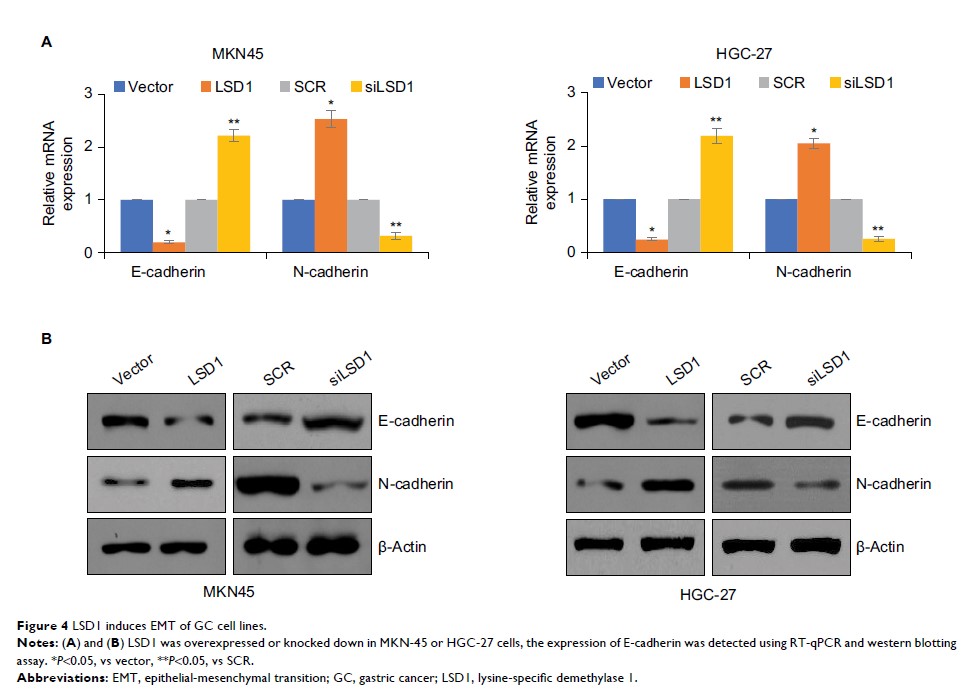
LSD1 的上调有利于 EMT 促进胃癌的迁移和侵袭
Authors Zhang J, Zhao D, Li Q, Du X, Liu Y, Dai X, Hong L
Received 6 September 2018
Accepted for publication 10 December 2018
Published 15 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4481—4491
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S186649
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Andrew Yee
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Xueqiong Zhu
Background: Gastric
cancer (GC) is a common malignant tumor of the digestive system. In addition,
GC metastasis is an extremely complicated process. A previous study has found
that lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) is abnormal expression in a variety
of cancers and its overexpression correlates with aggressive disease and poor
outcome.
Methods: qRT-PCR
and Western blot assays were used to assess the expression of LSD1 in GC tissue
samples and cell lines. Colony formation assay, CCK-8 assay, scratch-wound
assay and transwell invasion, were performed to determine the effect of LSD1 on
cell proliferation and migration as well as invasion in GC.
Results: Our
results show that LSD1 was up-regulated in GC tumor tissues and cell lines, and
high expression level of LSD1 was found to be positively correlated with tumor
size, lymph node metastasis and pathological grade. Moreover, LSD1 promoted
cell proliferation, migration and invasion of GC. In addition, LSD1 regulated
E-cadherin expression through demethylating H3K4me2, thereby promoting EMT in
GC.
Conclusion: Our work
indicated that LSD1 may be used as a potential target of gastric cancer.
Keywords: LSD1,
EMT, E-cadherin, H3K4me2, gastric cancer