110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

对中国南方的一所大型眼科专科中心的孤立病原体和微生物角膜炎抗生素敏感性历时 9 年的分析
Authors Lin L, Duan F, Yang Y, Lou B, Liang L, Lin X
Received 26 February 2019
Accepted for publication 16 April 2019
Published 15 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1295—1302
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S206831
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Professor Suresh Antony
Purpose: To
analyze the genus profile of isolated pathogens and antibiotic susceptibility trends
of microbial keratitis over nine years at a large referral eye center in
southern China.
Methods: Data of
corneal specimens from January 2010 to August 2018 of patients clinically
diagnosed with infectious keratitis were obtained from the center’s microbiology
database. Results with positive cultures along with antibiotic susceptibility
were reviewed and analyzed.
Results: We
collected and reviewed 7,229 specimens, including 3,092 with positive cultures.
Among them, 1,630 (52.72%) were bacterial, 1781 (57.60%) were fungal, and 319
(10.32%) were coinfected. A significant decreasing trend was observed in the
isolates of Gram-positive cocci (r =−0.711, P =0.032), among
which the proportion of coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CNS) was also
reduced (r =−0.883, P =0.002). In contrast, an increasing trend in the
proportion of Gram-negative bacilli was observed (r=0.661, P =0.053). The
susceptibility rates of Gram-positive cocci to cephalosporins were near 90%,
which was relatively high compared to fluoroquinolones. Fluoroquinolones
represented the antibiotics to which Gram-negative bacilli were the most
susceptible. Their susceptibility to moxifloxacin was 78.79%. The overall
performance of aminoglycosides and vancomycin was both around 70%. The
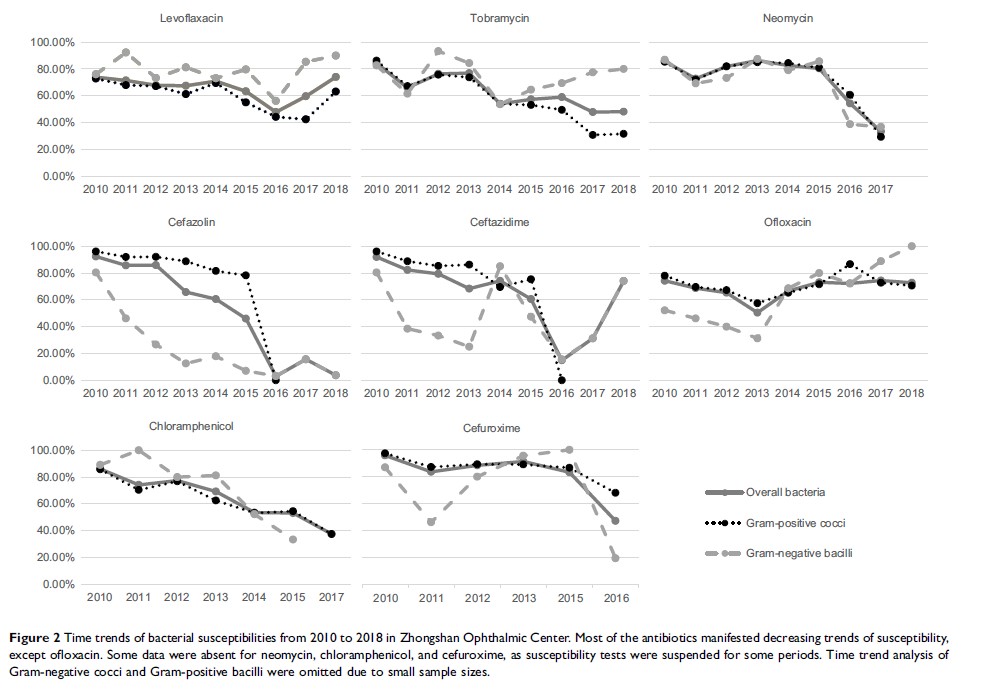
susceptibility of Gram-positive cocci to several antibiotics including
levofloxacin (r=−0.717, P =0.03), tobramycin (r= −0.933, P <0.001),
cefazolin (r= −0.964, P <0.001), ceftazidime (r=−0.929, P =0.003),
chloramphenicol (r=−0.929, P =0.003), and cefuroxime (r=−0.829, P =0.042) decreased
over time. The susceptibility of Gram-negative bacilli to ofloxacin increased
over time (r=0.854, P =0.004), whereas that to cefazolin (r=−0.833, P =0.005) and
chloramphenicol (r=−0.886, P =0.019) decreased over time.
Conclusion: From 2010
to 2018 in Zhongshan Ophthalmic Center, most isolates from infectious keratitis
were Gram-positive cocci (mainly CNS), which decreased over time, with an
increase in Gram-positive bacilli. More than half of the antibiotics showed
reducing trend of susceptibilities, and the antibiotic resistance situation in
southern China was not encouraging.
Keywords: infectious
keratitis, bacterial keratitis, antibiotic resistance, time trend