110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

七氟醚后处理通过在 Ezh2 调节下的自噬减轻新生大鼠缺氧缺血性脑损伤
Authors Xue H, Xu Y, Wang S, Wu ZY, Li XY, Zhang YH, Niu JY, Gao QS, Zhao P
Received 6 December 2018
Accepted for publication 4 March 2019
Published 15 May 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1691—1706
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S197325
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: When
neonatal rats suffer hypoxic-ischemic brain injury (HIBI), autophagy is
over-activated in the hippocampus, and inhibition of autophagy provides
neuroprotection. The aim of this study was to investigate the possible roles of
autophagy and Ezh2-regulated Pten/Akt/mTOR pathway in sevoflurane
post-conditioning (SPC)-mediated neuroprotection against HIBI in neonatal rats.
Methods: Seven-day-old
Sprague–Dawley rats underwent left common artery ligation followed by 2 h
hypoxia as described in the Rice–Vannucci model. The roles of autophagy and the
Ezh2-regulated Pten/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in the neuroprotection conferred
by SPC were examined by left-side intracerebroventricular injection with the
autophagy activator rapamycin and the Ezh2 inhibitor GSK126.
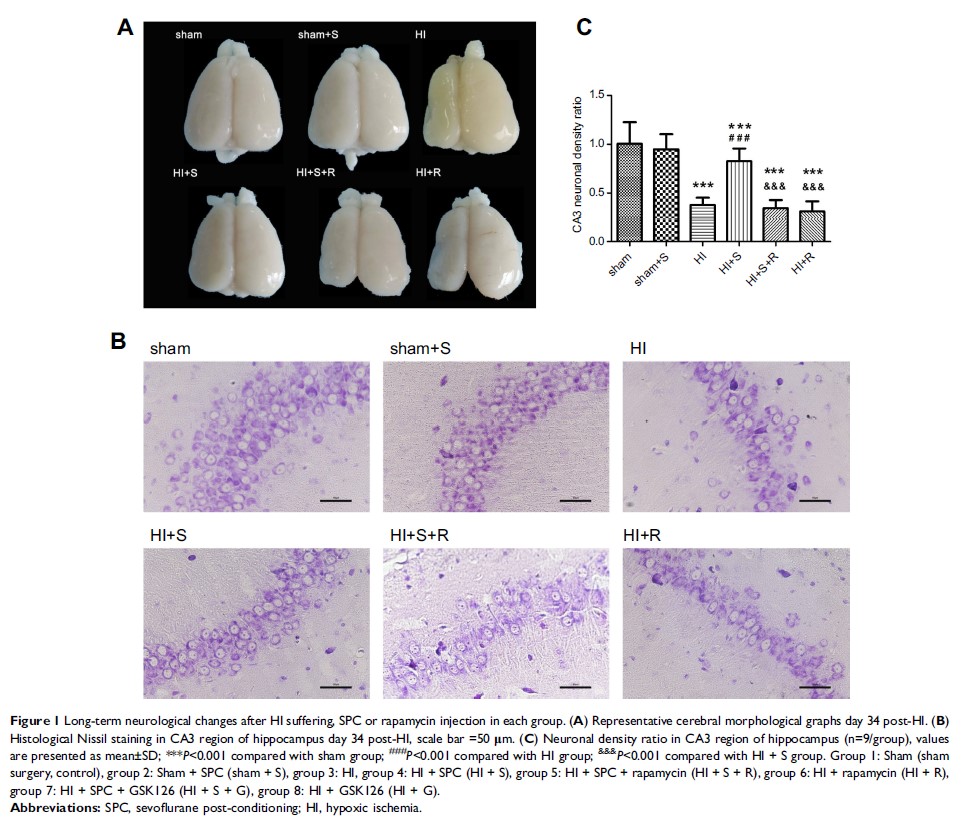
Results: SPC was
neuroprotective against HIBI through the inhibition of over-activated autophagy
in the hippocampus as characterized by the rapamycin-induced reversal of
neuronal density, neuronal morphology, cerebral morphology, and the expression
of the autophagy markers, LC3B-II and Beclin1. SPC significantly increased the
expression of Ezh2, H3K27me3, pAkt, and mTOR and decreased the expression of
Pten induced by HI. The Ezh2 inhibitor, GSK126, significantly reversed the
SPC-induced changes in expression of H3K27me3, Pten, pAkt, mTOR, LC3B-II, and
Beclin1. Ezh2 inhibition also reversed SPC-mediated attenuation of neuronal
loss and behavioral improvement in the Morris water maze.
Conclusion: These
results indicate that SPC inhibits excessive autophagy via the regulation of
Pten/Akt/mTOR signaling by Ezh2 to confer neuroprotection against HIBI in
neonatal rats.
Keywords: sevoflurane
post-conditioning, hypoxic-ischemic brain injury, neonatal rat, autophagy,
Ezh2, Pten/Akt/mTOR