110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

快速合成新型 siRNA 和多柔比星组合递送系统,用于协同抗癌作用
Authors Chen M, Wang L, Wang F, Li F, Xia W, Gu H, Chen Y
Received 21 December 2018
Accepted for publication 11 April 2019
Published 15 May 2019 Volume 2019:14 Pages 3557—3569
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S198511
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Lei Yang
Purpose: Combining siRNA and other
chemotherapeutic agents into one nanocarrier can overcome the multidrug
resistance (MDR) phenomenon by synergistically MDR relative genes silencing and
elevated chemotherapeutic activity. Most of these systems are typically
fabricated through complicated procedures, which involves materials
preparation, drug loading and modifications. Herein, the purpose of this study
is to develop a new and fast co-delivery system of siRNA and doxorubicin for
potentially synergistic cancer treatment.
Methods: The
co-delivery system is constructed conveniently by a stable complex consisting
of doxorubicin bound to siRNA via intercalation firstly, followed by
interacting with (3-Aminopropyl)triethoxysilane (APTES) electrostatically and
Tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) co-condensed, and the characterizations of the
resultant nanocarrier are also investigated. Furthermore, this study evaluates
the synergistic anti-cancer efficacy in MCF-7/MDR cells after treatment of
siRNA and doxorubicin ‘two in one’ nanocarriers.
Results: We
establish a new and fast method to craft a co-delivery system of siRNA and
doxorubicin with controllable and nearly uniform size, and the entire
fabrication process only costs in about 10 minutes. The resultant co-delivery
system presents high loading capacities of siRNA and doxorubicin, and the
encapsulated doxorubicin plays a pH-responsive control release. Further,
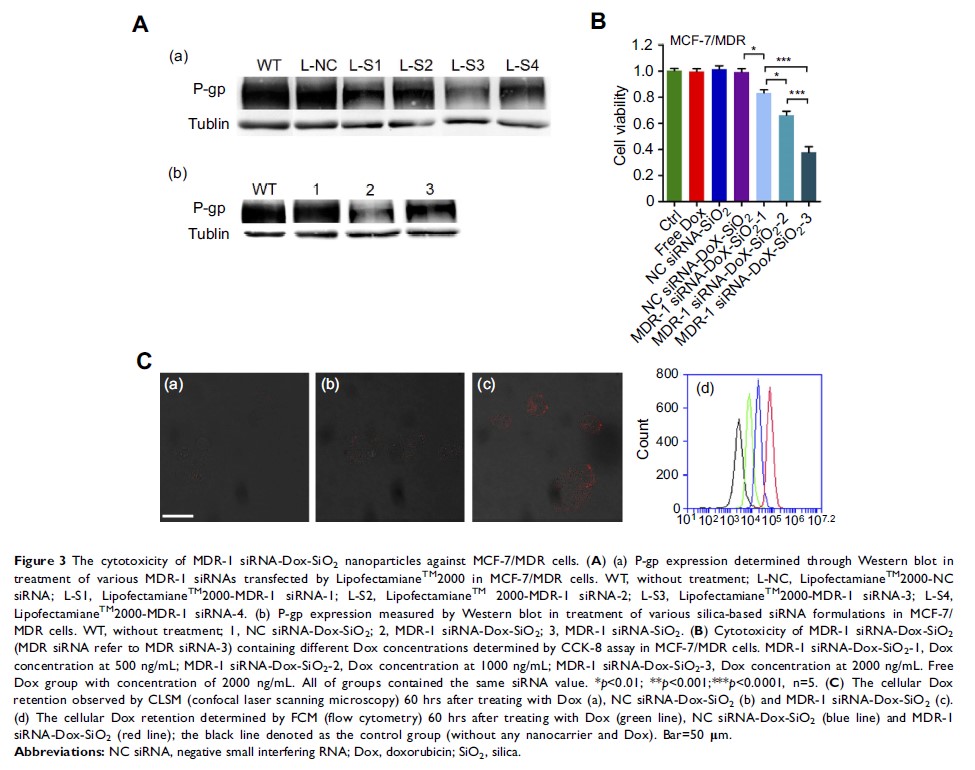
biological functionality tests of the synthesized co-delivery nanocarriers show
high inhibition of P-gp protein encoded by MDR-1 gene in MCF-7/MDR cells (a
variant of human breast cancer cell line with drug resistance) after
transfection of these nanocarriers carrying MDR-1 siRNA and doxorubicin
simultaneously, which sensitize the MCF-7/MDR cells to doxorubicin, overall
leading to improved cell suppression.
Conclusion: Collectively,
this co-delivery system not only serves as potent therapeutics for synergistic
cancer therapy, it also may facilitate the bench-to-bedside translation of
combinatorial delivery system as a robust drug nanocarrier by allowing for
fabricating a simply and fast nanocarrier for co-delivery of siRNA and
doxorubicin with predictable high production rate.
Keywords: siRNA,
doxorubicin, codelivery system, multidrug resistance, cancer therapy