110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

癌蛋白 HBXIP 通过激活 MMP15 表达促进肝细胞癌细胞的转移
Authors Zheng S, Wu H, Wang F, Lv J, Lu J, Fang Q, Wang F, Lu Y, Zhang S, Xu Y, Bao Q, Xie C, Yin Z
Received 19 December 2018
Accepted for publication 21 March 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4529—4540
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S198783
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Kenan Onel
Background: Due to
the high recurrence and metastasis rate, the clinical outcomes of patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are still unsatisfactory. Hepatitis B virus
X-interacting protein (HBXIP) has been reported to play crucial roles in
carcinogenesis.
Purpose: We aimed
to reveal the functional significance and underlying mechanism of HBXIP in HCC
metastasis.Methods: Cell transwell assay, in vivo metastasis model, real-time
PCR, western blot analysis, luciferase reporter and chromatin
immunoprecipitation assays were applied.
Results: Here, we
detected the HBXIP expression level and determined its clinical significance in
HCC. We found that HBXIP was significantly upregulated in HCC tissues, and
correlated with vascular invasion, tumor metastasis and worse prognosis of HCC
patients. HBXIP enhanced cell migration and invasion in vitro, and promoted the
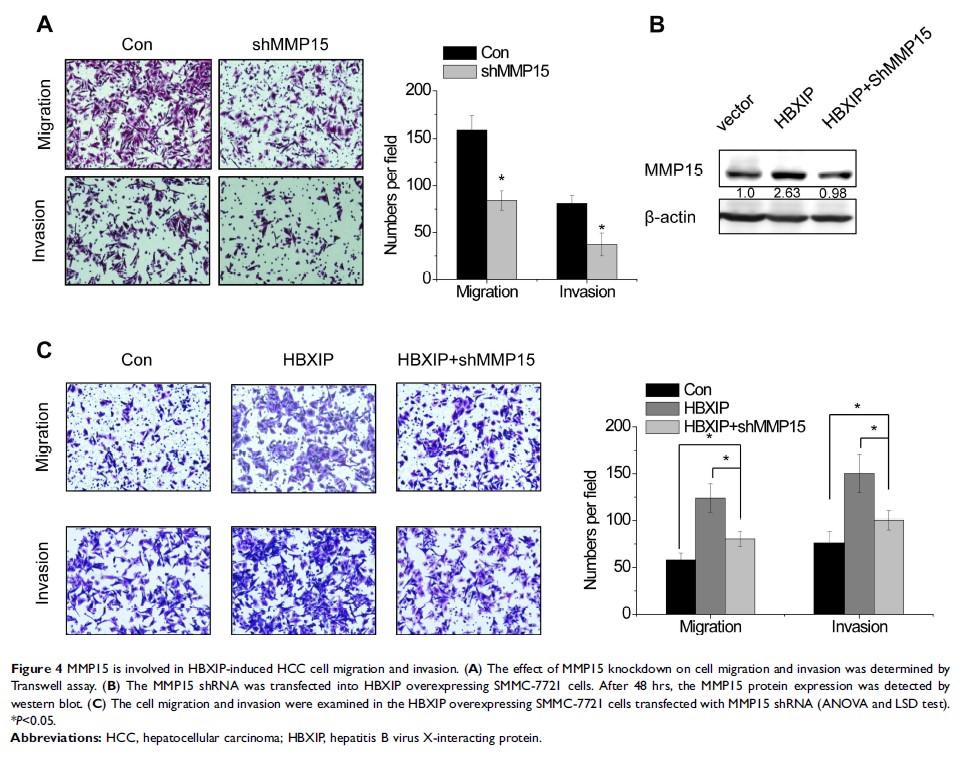
metastasis of HCC in vivo. Furthermore, we confirmed that HBXIP increased MMP15
expression through association with proto-oncogene c-myc. Depletion of c-myc
abolished HBXIP-mediated MMP-15 upregulation. We also observed a positive
correlation between HBXIP and MMP15 expression in HCC tissues.
Conclusion: Our
results establish a novel function for HBXIP-MMP15 regulation in HCC metastasis
and suggest its candidacy as a new prognostic biomarker and therapeutic target
for HCC metastasis.
Keywords: c-myc,
MMP15, HBXIP, metastasis