110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

使甲胎蛋白(AFP)增高的结直肠癌的临床病理特征和预后:对 20 个病例的临床分析
Authors Ren F, Weng W, Zhang Q, Tan C, Xu M, Zhang M, Wang L, Sheng W, Ni S, Huang D
Received 4 December 2018
Accepted for publication 12 April 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:11 Pages 4557—4567
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S196919
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Cristina Weinberg
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Beicheng Sun
Background: High
serum levels of alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) are observed in some gastrointestinal
cancers. However, primary AFP-producing colorectal cancer (CRC) is extremely
rare and causes confusion among clinicians. In this study, we analyzed the
clinicopathological features and clinical outcomes of AFP-producing CRC and
provide a brief view of this rare carcinoma.
Patients and methods: Twenty
patients with AFP-producing CRC were enrolled at the Fudan University Shanghai
Cancer Center from 2012 to 2015. Clinical information, including serum AFP and
CEA levels, and outcomes were collected. Tumors were divided into three
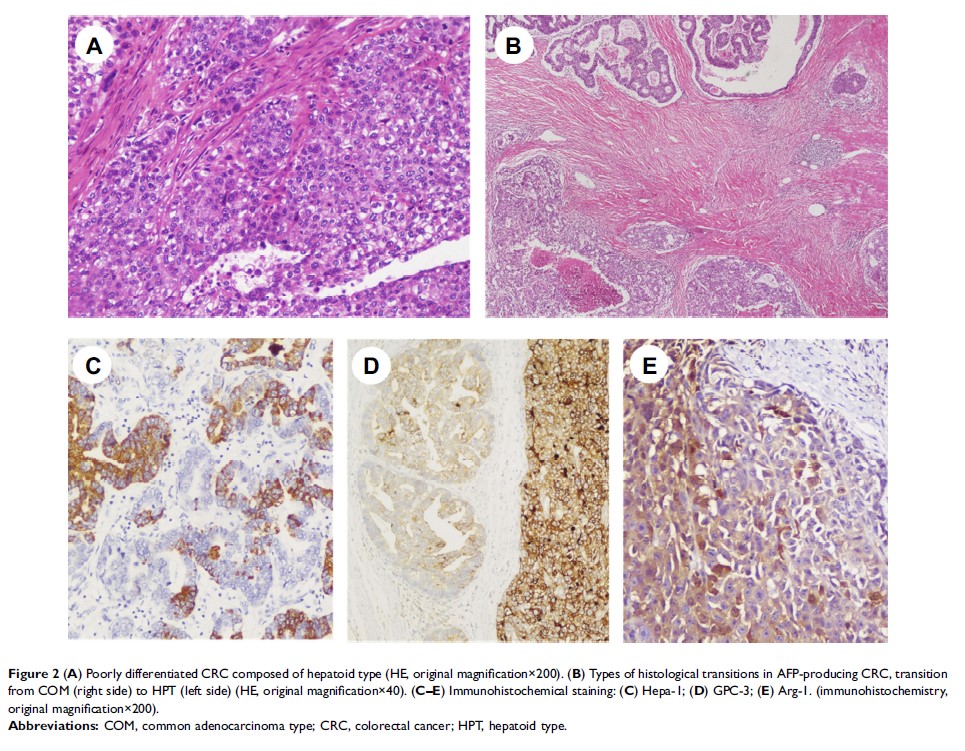
histologic types: the common adenocarcinoma (COM) type, mucinous adenocarcinoma
type and hepatoid type (HPT). Immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of GPC3,
Hepa-1, SALL4 and Arg-1 was performed. Additionally, mutations of the KRAS,
NRAS and BRAF genes were examined. Finally, another 40 stage-matched patients
with traditional CRC were enrolled as controls for survival analysis.
Results: AFP-producing
CRC was more likely to occur in males (60%) and arose mainly from the ascending
(40%) and sigmoid (35%) colon. In addition, the majority of patients with
AFP-producing CRC had poor differentiation (50%), advanced local invasion (80%)
and lymph node (LN) metastasis (60%). Synchronous distant metastasis was
commonly observed (35%). Interestingly, serum AFP levels were closely
associated with LN metastasis. Histopathologically, the COM type was the most
common pattern. In IHC staining, the HPT pattern was the most distinct due to
high positivity rates of GPC3, Hepa-1 and Arg-1. One patient had mismatch
repair deficiency, and another had a KRAS mutation. Patients with AFP-producing
CRC had worse progression-free and overall survival than patients with traditional
CRC.
Conclusion: AFP-producing
CRC has unique clinical and histopathological characteristics, showing an
aggressive biological behavior and worse prognosis than traditional CRC.
Keywords: AFP-producing
colorectal cancer, clinicopathological features, serum AFP, prognosis