110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

中国南方深圳儿童患者中携带的超广谱 β-内酰胺酶(ESBLs)大肠埃希氏菌 blaCTX-M 基因分型及相应耐药特征
Authors Patil S, Chen X, Lian M, Wen F
Received 29 December 2018
Accepted for publication 10 April 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 1325—1332
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/IDR.S199861
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 2
Editor who approved publication: Dr Joachim Wink
Aims and Objectives: The
emergence and spread of extended-spectrum β-lactamases (ESBLs) particularly
CTX-M producing multi-drug-resistant (MDR) Escherichia coli (E. coli ) is one of
the greatest challenges for community health globally. The study investigated
the phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of ESBLs-producing E. coli recovered
from pediatric patients from Shenzhen Children’s Hospital, China.
Materials and methods: Present
study, a total of 2,670 isolates of E. coli were collected from Shenzhen Children’s
Hospital, China of which 950 were ESBLs producer. ESBLs production was
confirmed by using the combination disc diffusion method, and antimicrobial
susceptibility test was detected. In addition, β-lactamase-producing genes and
co-existence of carbapenem/colistin resistance genes were determined by PCR
assay and sequencing. The diversity and phylogenetic relationship were
determined by multi-locus sequence typing method.
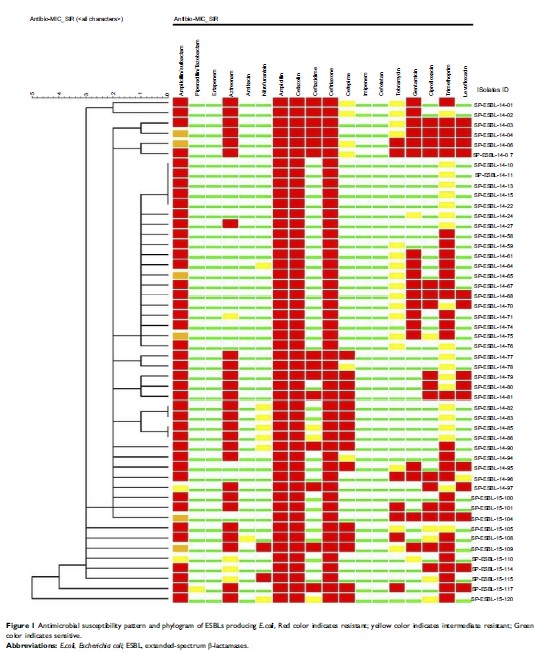
Results: Thirty-five
percent (n =950)
prevalence of ESBLs-producing E. coli we reported in Shenzhen, China of which 50
ESBLs producing E. coli were randomly selected for a further
characterization. All 50 ESBLs- producing E. coli isolates
revealed MDR phenotype and 100% were resistant to Ampicillin/sulbactam,
Ampicillin, Cefazolin, and Ceftriaxone. All 50 ESBLs producers harbored at
least one type of β-lactamase gene particular bla CTX-M. The PCR and
sequencing revealed the most common CTX-M subtype was blaCTX-M-15 (n =18), followed by blaCTX-M-14 (n =16), blaCTX-M-90 (n =9), blaCTX-M-55 (n =3), blaCTX-M-27 , blaCTX-M-101 , and blaCTX-M-211 each (n =1). Co-existence of bla CTX-M with bla TEM , bla SHV , bla GES , and bla VEB was
detected in few isolates. Among identified sequence types, ST131 (12%) was more
dominant in ESBLs-producing E. coli . Phylogenetic group A was the most prominent
group among the ESBLs-producing E. coli based on multiplex PCR.
Conclusion: Our study
shows the prevalence of bla CTX-M gene in
ESBLs-producing E. coli in pediatric patients in Shenzhen, China.
We highlight the importance to monitor the emergence and trends of
ESBLs-producing isolates in a pediatric healthcare setting.
Keywords: Antimicrobial
resistance, molecular characterization, MLST, ESBLs, Escherichia coli