110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

穿心莲内酯通过保持 Akt/mTOR 活性来减弱布比卡因诱导的 SH-SY5Y 细胞的细胞毒性
Authors Zhang H, Wang W, Du Q
Received 10 January 2019
Accepted for publication 3 April 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:13 Pages 1659—1666
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S201122
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Colin Mak
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Qiongyu Guo
Background: Bupivacaine
(Bup) is the most commonly used local anesthetic. However, Bup induces
cytotoxicity, especially in older patients. Recent reports have indicated that
andrographolide (Andro) exhibits protective effects on human neurons.
Nevertheless, whether Andro can inhibit Bup-induced cytotoxicity remains
unclear. As such, we investigated the effect of Andro on Bup-induced cytotoxicity
of SH-SY5Y cells in the present study.
Methods: Western
blotting was used to examine expression of Bax, Bcl2, active caspase 3, p-Akt,
and p-mTOR in SH-SY5Y cells. In addition, ELISA was used to detect levels of
total glutathione and reactive oxygen species in cells.
Results: We found
that Andro attenuated Bup-induced cytotoxicity of SH-SY5Y cells. In addition,
Andro inhibited Bup-induced apoptosis via downregulating the expression of Bax
and active caspase 3 and upregulating the proteins Bcl2, p-Akt, and p-mTOR in
SH-SY5Y cells. Moreover, Andro alleviated Bup-induced oxidative damage in
SH-SY5Y cells via downregulating the level of reactive oxygen species and
upregulating of the level of total glutathione. More significantly, inhibition
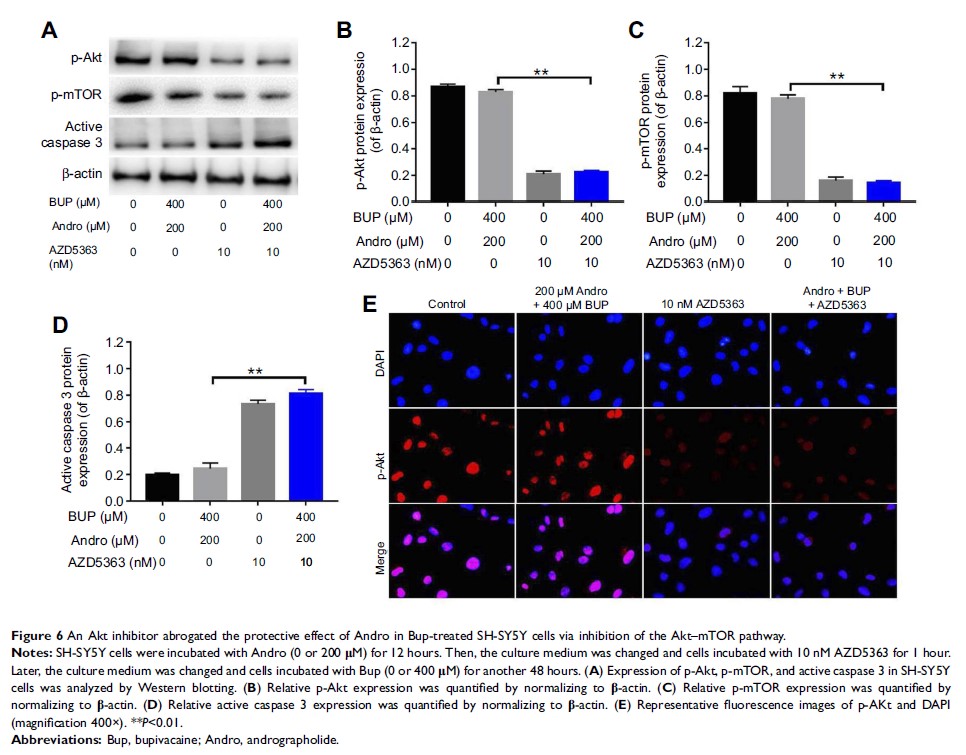
of Akt abolished the protective effect of Andro in Bup-treated SH-SY5Y cells.
Conclusion: Our
findings indicated that Andro played a neuroprotective role via preserving
Akt/mTOR activity and increasing antioxidative status in Bup-treated SH-SY5Y
cells. Therefore, Andro may be a potential agent for the treatment of human
cytotoxicity induced by Bup.
Keywords: andrographolide,
bupivacaine, apoptosis, Akt, cytotoxicity