110932
论文已发表
注册即可获取德孚的最新动态
IF 收录期刊
- 3.4 Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press)
- 3.2 Clin Epidemiol
- 2.6 Cancer Manag Res
- 2.9 Infect Drug Resist
- 3.7 Clin Interv Aging
- 5.1 Drug Des Dev Ther
- 3.1 Int J Chronic Obstr
- 6.6 Int J Nanomed
- 2.6 Int J Women's Health
- 2.9 Neuropsych Dis Treat
- 2.8 OncoTargets Ther
- 2.0 Patient Prefer Adher
- 2.2 Ther Clin Risk Manag
- 2.5 J Pain Res
- 3.0 Diabet Metab Synd Ob
- 3.2 Psychol Res Behav Ma
- 3.4 Nat Sci Sleep
- 1.8 Pharmgenomics Pers Med
- 2.0 Risk Manag Healthc Policy
- 4.1 J Inflamm Res
- 2.0 Int J Gen Med
- 3.4 J Hepatocell Carcinoma
- 3.0 J Asthma Allergy
- 2.2 Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol
- 2.4 J Multidiscip Healthc

辐照可提高肺癌细胞的免疫原性,基于辐射的肿瘤细胞疫苗在体内引发肿瘤抗原特异性 T 细胞反应
Authors Luo L, Lv M, Zhuang X, Zhang Q, Qiao T
Received 8 December 2018
Accepted for publication 8 March 2019
Published 16 May 2019 Volume 2019:12 Pages 3805—3815
DOI https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S197516
Checked for plagiarism Yes
Review by Single-blind
Peer reviewers approved by Dr Amy Norman
Peer reviewer comments 3
Editor who approved publication: Dr Takuya Aoki
Background: During
the past decades, great efforts have been built to develop lung cancer
vaccines. Whole tumor cell lysate (TCL) are ideal sources of antigens for
cancer vaccine design, which however have limited efficacy due to insufficient
immunogenicity. Recently, radiotherapy has been closely related to immunotherapy.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the regulatory effect of irradiation (IR) on
tumor immune response.
Purpose: To
explore the immunogenicity modulation effect of IR on lung cancer cells.
Methods: RNA-sequence
and qPCR assay was used to evaluate the change of tumor antigens expression
after repeated X rays radiation on A549 cells. Vaccine based on TCL of
irradiated Lewis lung cancer cells (IR-LLC) was established; therapeutic effect
of TCL (IR-LLC) was examined in xenografted tumor model of mice. Flow cytometry
was conducted to evaluate the rate of immune cells in spleen; ELISA was used to
detect the level of cytokines in plasma. Immunohistochemistry was performed to
evaluate the infiltrations of T-cell in tumor tissues; TIMER analysis was used
to explore the correlations between tumor antigen expressions and the
abundances of immune infiltrates.
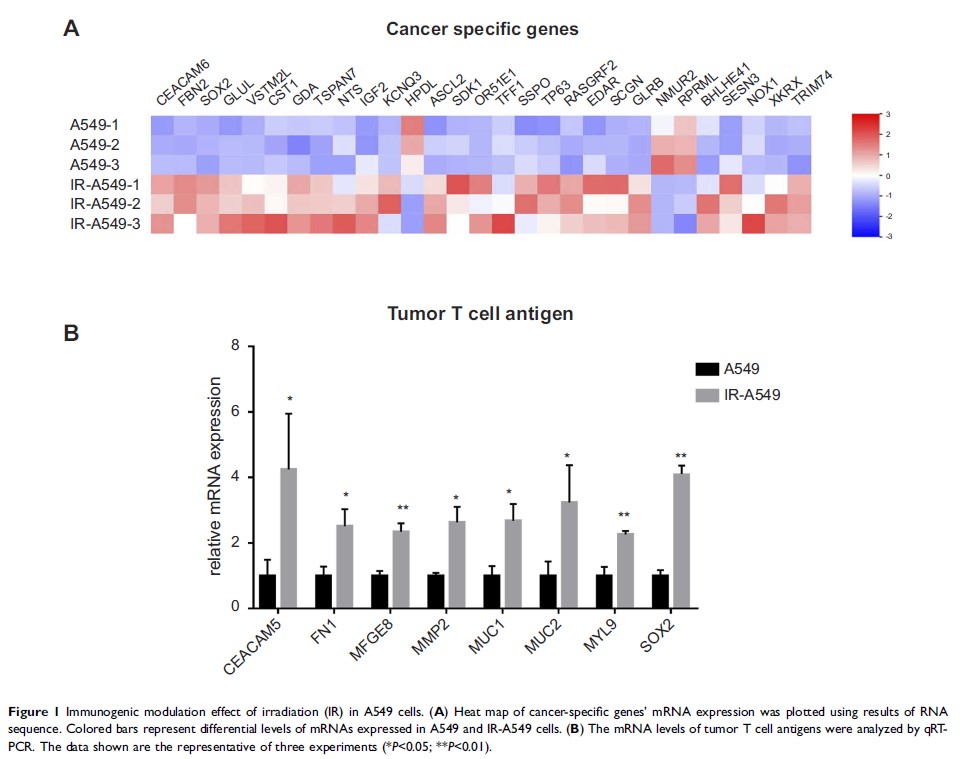
Results: IR
upregulated the expression of tumor antigens in A549 cells. Compared to the
control group and unirradiated tumor cell vaccine, TCL(IR-LLC) had a significantly
stronger anti-tumor effect in mice bearing with LLC xenografts. TCL(IR-LLC)
significantly increased matured DCs and total CD4+ T cells but downregulated
Tregs and PD-1+ CD8+ T cells in mice spleen; TCL(IR-LLC) vaccine upregulated
the level of IFN-γ and IL-4 while decreased IL-10 in serum; increased
infiltrations of CD4+ T-cells and CD8+ T-cells were observed in the tumor
issues of mice immunized with TCL(IR-LLC). Tumor antigens including FN1, MFGE8,
MMP2, MYL9 may contribute to the enhanced T-cell response.
Conclusion: This
study confirmed the immunogenicity modulation effect of IR in NSCLC cells,
indicating IR might be an effective strategy to enhance the anti-tumor immunity
of cancer cell vaccine.
Keywords: lung
cancer, whole tumor cell vaccine, irradiation, tumor antigen, T cell